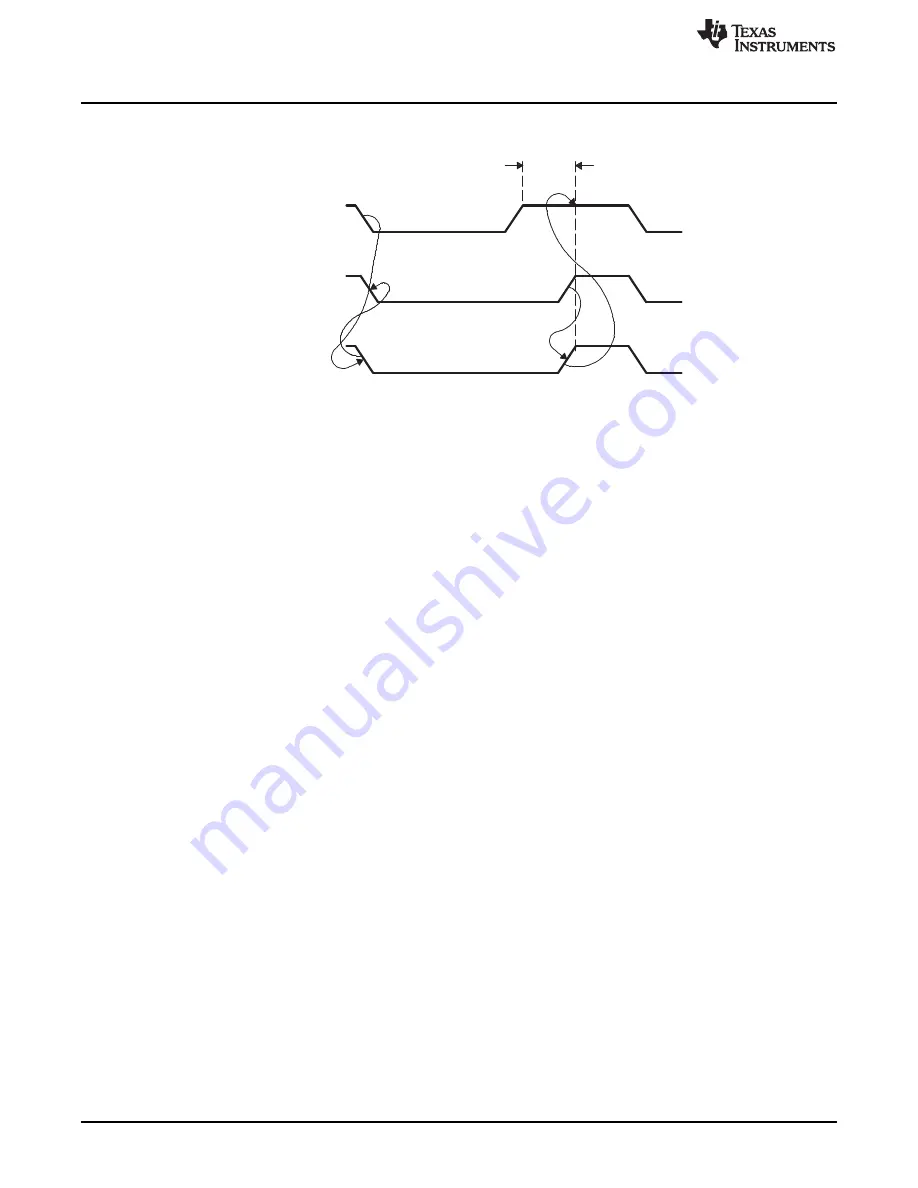
Wait
state
Start HIGH
period
I2Cx_SCL
from device #1
I2Cx_SCL
from device #2
Bus line
I2Cx_SCL
Functional Description
Figure 21-10. Synchronization of Two I2C Clock Generators
21.3.9 Prescaler (SCLK/ICLK)
The I2C module is operated with a functional clock (SCLK) frequency that can be in a range of 12-100
MHz, according to I2C mode that must be used (an internal ~24 MHz clock (ICLK) is recommended in
case of F/S operation mode e). Note that the frequency of the functional clock influences directly the I2C
bus performance and timings.
The internal clock used for I2C logic - ICLK - is generated via the I2C prescaler block. The prescaler
consists of a 4-bit register - I2C _PSC, and is used to divide the system clock (SCLK) to obtain the
internal required clock for the I2C module.
21.3.10 Noise Filter
The noise filter is used to suppress any noise that is 50 ns or less, in the case of F/S mode of operation. It
is designed to suppress noise with one ICLK. The noise filter is always one ICLK cycle, regardless of the
bus speed. For FS mode (prescaler = 4, ICLK = 24 MHz), the maximum width of the suppressed spikes is
41.6 ns. To ensure a correct filtering, the prescaler must be programmed accordingly.
21.3.11 I2C Interrupts
The I2C module generates 12 types of interrupt: addressed as slave, bus free (stop condition detected),
access error, start condition, arbitration-lost, noacknowledge, general call, registers-ready-for-access,
receive and transmit data, receive and transmit draining. These 12 interrupts are accompanied with 12
interrupt masks and flags defined in the I2C_IRQENABLE_SET and respectively I2C_IRQSTATUS_RAW
registers. Note that all these 12 interrupt events are sharing the same hardware interrupt line.
•
Addressed As Slave interrupt (AAS) is generated to inform the Local Host that an external master
addressed the module as a slave. When this interrupt occurs, the CPU can check the I2C_ACTOA
status register to check which of the 4 own addresses was used by the external master to access the
module.
•
Bus Free interrupt (BF) is generated to inform the Local Host that the I2C bus became free (when a
Stop Condition is detected on the bus) and the module can initiate his own I2C transaction.
•
Start Condition interrupt (STC) is generated after the module being in idle mode have detected
(synchronously or asynchronously) a possible Start Condition on the bus (signalized with WakeUp).
•
Access Error interrupt (AERR) is generated if a Data read access is performed while RX FIFO is empty
or a Data write access is performed while TX FIFO is full.
•
Arbitration lost interrupt (AL) is generated when the I2C arbitration procedure is lost.
•
No-acknowledge interrupt (NACK) is generated when the master I2C does not receive acknowledge
from the receiver.
•
General call interrupt (GC) is generated when the device detects the address of all zeros (8 bits).
•
Registers-ready-for-access interrupt (ARDY) is generated by the I2C when the previously programmed
address, data, and command have been performed and the status bits have been updated. This
3708
I2C
SPRUH73H – October 2011 – Revised April 2013
Copyright © 2011–2013, Texas Instruments Incorporated
















































