p
f
F
α
∫
x n
1
1
n
2
1
–
,
–
,
(
)
dx
=
p
f
0
F
∫
x n
1
1
n
2
1
–
,
–
,
(
)
dx
=
p
2
---
f x n
1
1
n
2
1
–
,
–
,
(
)
x
d
0
L
bnd
∫
f x n
1
1
n
2
1
–
,
–
,
(
)
x
d
U
bnd
∞
∫
=
=
t
x
1
x
2
–
S
----------------
=
S
Sx
1
2
n
1
-----------
Sx
2
2
n
2
-----------
+
=
df
Sx
1
2
n
1
-----------
Sx
2
2
n
2
-----------
+
⎝
⎠
⎜
⎟
⎛
⎞
2
1
n
1
1
–
--------------
Sx
1
2
n
1
-----------
⎝
⎠
⎜
⎟
⎛
⎞
2
1
n
2
1
–
--------------
Sx
2
2
n
2
-----------
⎝
⎠
⎜
⎟
⎛
⎞
2
+
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
=
Appendix B: Reference Information
386
2
-
Samp
Ü
Test
for the alternative hypothesis
.
2
-
Samp
Ü
Test
for the alternative hypothesis
.
2
-
Samp
Ü
Test
for the alternative hypothesis
s
1
ƒ s
2
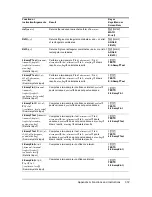
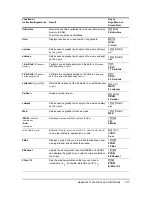
. Limits must satisfy the following:
where: [
Lbnd,Ubnd
] = lower and upper limits
The
Ü
-statistic is used as the bound producing the smallest integral. The remaining bound is
selected to achieve the preceding integral’s equality relationship.
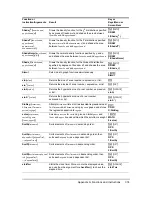
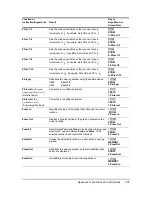
2-SampTTest
The following is the definition for the
2-SampTTest
. The two-sample
t
statistic with degrees of
freedom
df
is:
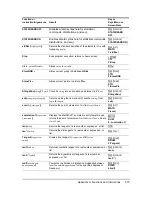
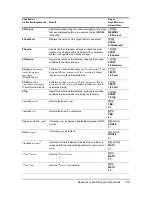
where the computation of
S
and
df
are dependent on whether the variances are pooled. If the
variances are not pooled:
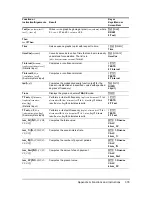
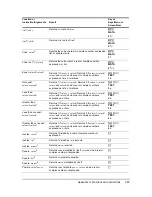
df
(
x, ,
) =
Û
( ) with degrees of freedom
df
, ,
and
p
= reported
p
value
n
1
1
–
n
2
1
–
n
1
1
–
n
2
1
–
σ
1
σ
2
>
σ
1
σ
2
<