October 2017
RiverPro and RioPro ADCP Guide
Page 104
EAR-Controlled Technology Subject to Restrictions Contained on the Cover Page.
Recorder Commands
The recorder contains approximately 16 megabytes of solid-state nonvolatile memory, which can be used
to record data. If more data is collected than fits in the memory, the newest data will not be recorded.
Once the recorder fills up, the recorder MUST be erased before re-deploying the RiverPro/RioPro (start
pinging again).
If the RiverPro/RioPro is set to record data (
) and the recorder is full, the RiverPro/RioPro
will
not
start pinging and will return a
RECORDER NOT READY
message.
Using the recorder will slow down the RiverPro/RioPro’s ping rate.
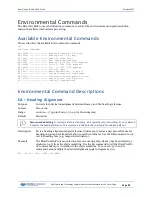
Available Recorder Commands
This section lists the available Recorder commands.
>m?
Available Commands:
ME ---------------------- ErAsE recorder
MM ---------------------- Show memory usage
MN RP ------------------- Set deployment name [1..6 characters]
MR 0 -------------------- Set recorder on/off [0=off,1=on]
MQ ---------------------- Streaming Download (addr, nbytes)
MY ---------------------- Y-Modem Download
M? ---------------------- Display M-Command Menu
Recorder Command Descriptions
This section lists the Recorder commands.
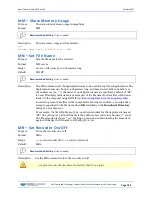
ME – Erase Recorder
Purpose
Erase the contents of the loop recorder.
Format
ME ErAsE
Recommended Setting
. Use as needed.
Description
ME ErAsE erases the recorder memory. To make it more difficult to accidentally erase the
data, the word “erase” must be typed with exactly one space after the “ME” (which is not
case sensitive) and with alternating upper and lower case letters, as shown.
Once erased, data is not recoverable.
Erasing the loop-recorder will take several minutes, and no status updates are provided
during the erase process. When complete, the status will be displayed on screen as shown
below.
>me ErAsE
Erasing recorder (may take a few minutes)...
Erasing recorder (may take a few minutes)... Recorder erased.
Erasing recorder (may take a few minutes)... ERR: Can’t erase recorder.
>