User Guide
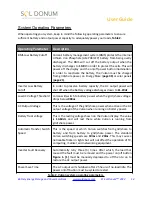
Grid/Shore Standby Power
Most applications of Vulcan units see use as a passive power protection/standby backup to
critical loads that run on grid/shore power. In this arrangement, Vulcan can also improve power
quality and continuity of operations through EMI filtering and by switching to battery power in
the event of a loss or drop of AC voltage. See section General Usage on page 15.
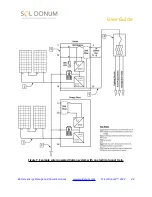
Time-of-Use/On-Peak Electricity Cost Reduction
Under time-of-use (TOU) rate plans, utility customers are charged more for the electricity used
during afternoon 'peak' hours when the demand for electricity is higher. The cheapest electricity
can be found during 'off-peak' hours when demand is lower. For example, summer off-peak
hours might be from 6pm until 2pm the following day because temperatures are lower and
fewer people need to cool their living space, creating less demand for electricity.
If you have TOU rates, you can lower your electric bills by waiting for the cheapest time of day
to use electricity. For example, using a 7 day digital timer rated at 120V/30A or an outlet timer
rated at 120V/15A,
Figure 8.
, you can schedule when to use battery power to run a clothes
washer or dishwasher, turn on the lights or charge an electric vehicle. The timer can be set to
charge the Vulcan at night during the 'off-peak' hours, depending on your utility’s specific rate
plan, with an operating life of 10 years or greater. Utilities offer TOU plans to reduce demand on
the electric grid by motivating their customers to reduce electricity use during peak hours.
Figure 8. Time-of-Use cost reduction. Add a timer to Vulcan to reduce electricity costs.
Battery Energy Storage and Power Solutions
© Sol Donum
™
2022
25