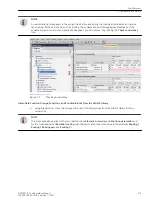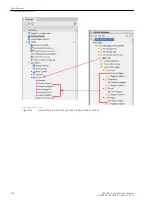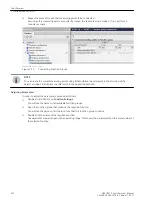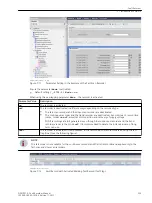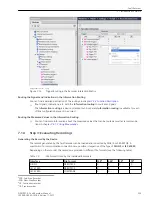
required. It can be necessary to connect additional measuring points to the function group, depending on the
nature of the user functions used. The configuration is done via the Function group connections editor in
DIGSI 5.
You can find more detailed information on this in chapter
2.1 Function Embedding in the Device
The function groups 3-phase voltage, Voltage/current 1-phase, and Voltage/current 3-phase have the
following interfaces to the measuring points:
•
3-phase voltage
The measurands from the 3-phase voltage system are supplied via this interface. Depending on the
connection type of the transformers, in the 3-phase voltage system these are, for example, V
A
, V
B
, V
C
.
•
Voltage/current 1-phase and Voltage/current 3-phase
The measurands from the 1-phase or the 3-phase voltage and current system are supplied via these inter-
faces. All values that can be calculated from the measurands are also provided via these interfaces.
•
Phasor Measurement Unit (PMU)
The measurands from the PMU are supplied via this interface.
Power-System Data and Function Groups and Functions that cannot be Configured
The power-system data and the PMU function group are visible, but cannot be changed.
Function Description
Input and Output Signals
Recordings are started on the fast-scan and slow-scan recorders if a trigger criterion is satisfied or a control
input is activated.
The fault recorder makes different input signals available, with which recordings can be specifically started
and deleted. The output signals provide information about the function status.
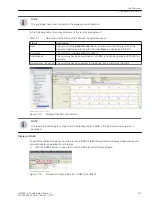
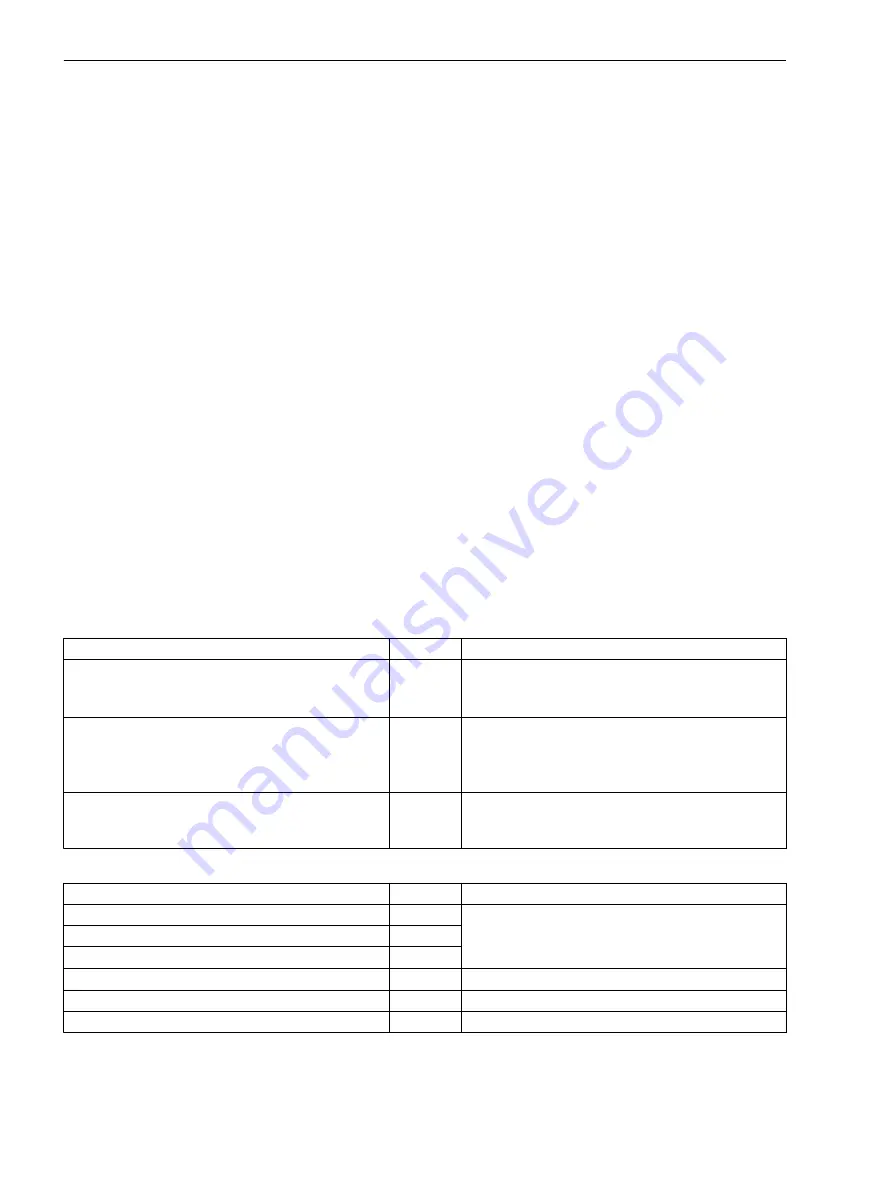
In the following table you can find input signals of the fault-recording functions:
Name
Type
Description
Control:
Start record
SPC
Start of a recording preferably via IEC 61850
The set pre and post-trigger time are taken into
account.
Control:
>External start
SPS
Start of a recording preferably via a binary input or a
logic block chart.
The set pre and post-trigger time are taken into
account.
Control:
>Manual start
SPS
Start of a recording with fixed time (
Manual
record time
parameter), preferably using a func-
tion key
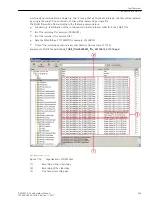
In the following table you can find output signals of the fault-recording functions:
Name
Type
Description
General:
Mode (controllable)
ENC
Status feedback of the fault recording according to
Chapter
General:
Behavior
ENS
General:
Health
ENS
Control:
Fault number
INS
Indication of the error number for current fault
Control:
Recording started
SPS
Fault recording running
Control:
Record made
SPS
End of recording
7.2.3
Fault Recorder
7.2 Function-Group Type Recorder
232
SIPROTEC 5, Fault Recorder, Manual
C53000-G5040-C018-5, Edition 11.2017
Содержание SIPROTEC 5
Страница 8: ...8 SIPROTEC 5 Fault Recorder Manual C53000 G5040 C018 5 Edition 11 2017 ...
Страница 18: ...18 SIPROTEC 5 Fault Recorder Manual C53000 G5040 C018 5 Edition 11 2017 ...
Страница 134: ...134 SIPROTEC 5 Fault Recorder Manual C53000 G5040 C018 5 Edition 11 2017 ...
Страница 212: ...212 SIPROTEC 5 Fault Recorder Manual C53000 G5040 C018 5 Edition 11 2017 ...
Страница 422: ...422 SIPROTEC 5 Fault Recorder Manual C53000 G5040 C018 5 Edition 11 2017 ...
Страница 426: ...426 SIPROTEC 5 Fault Recorder Manual C53000 G5040 C018 5 Edition 11 2017 ...
Страница 452: ...452 SIPROTEC 5 Fault Recorder Manual C53000 G5040 C018 5 Edition 11 2017 ...
Страница 490: ...490 SIPROTEC 5 Fault Recorder Manual C53000 G5040 C018 5 Edition 11 2017 ...