Supplementary information
18.8 Basics and terminology of fault-tolerant communication
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
322
System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC
Redundant communication system
The availability of the communication system can be increased by duplicating
subcomponents, duplicating all bus components, or using a fiber-optic ring.
Monitoring and synchronization mechanisms ensure that standby components take over
communication if one components fails.
A redundant communication system is required for the user of fault-tolerant S7 connections.
Fault-tolerant communication
Fault-tolerant communication is the use of S7 communication SFBs over fault-tolerance S7
connections.
A fault-tolerant S7 connection consists of at least two and a maximum of four partial
connections depending on networking. Two partial connections are established for fault-
tolerant communication; the two others are configuration standbys.
Fault-tolerant S7 connections require a redundant communication system.
Redundancy nodes
Redundancy nodes represent extreme reliability of communication between two fault-tolerant
systems. A system with multi-channel components is represented by redundancy nodes.
Redundancy nodes are independent when the failure of a component within the node does
not result in any reliability impairment in other nodes.
Even with fault-tolerant communication, only single errors/faults can be tolerated. If more
than one error occurs between two communication end points, communication can no longer
be guaranteed.
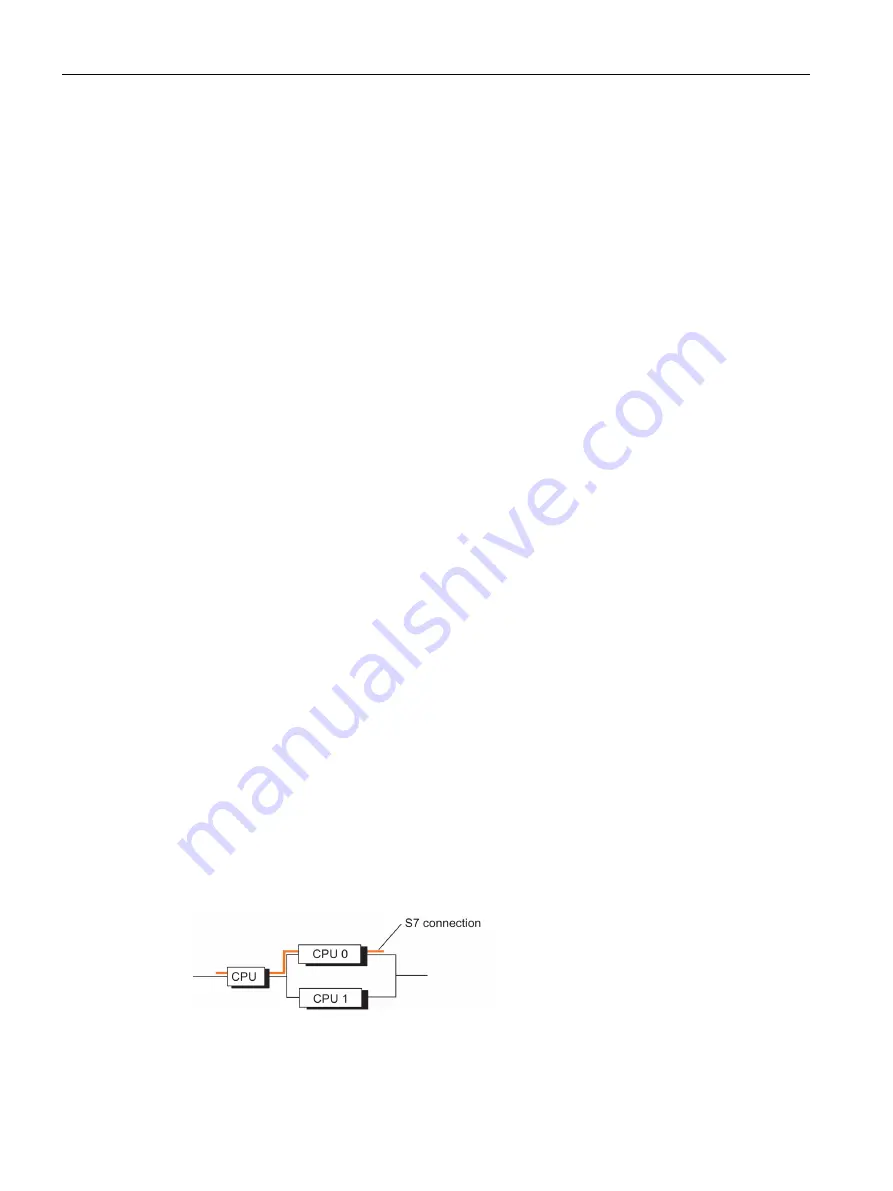
Connection (S7 connection)
A connection represents the logical assignment of two communication peers for executing a
communication service. Every connection has two end points containing the information
required for addressing the communication peer as well as other attributes for establishing
the connection.
An S7 connection is the communication connection between two standard CPUs or between
a standard CPU and a CPU of a fault-tolerant system.
Unlike a fault-tolerant S7 connection, which contains at least two partial connections, an S7
connection does only consist of one connection. If that connection fails, communication is
terminated.
Figure 18-6 Example of an S7 connection






























