17
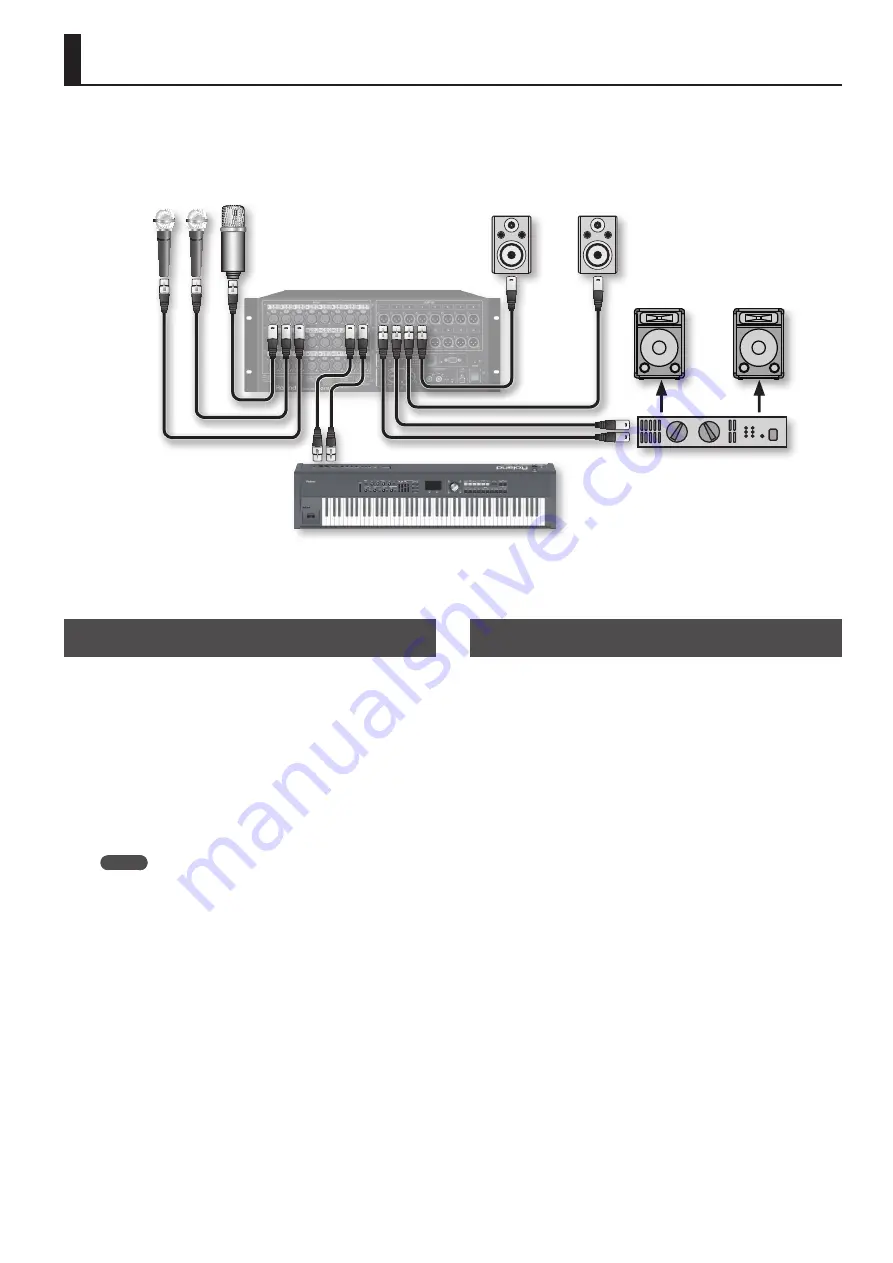
Connecting Devices
* To prevent malfunction and equipment failure, always turn down the volume, and turn off all the units before making any connections.
* This instrument is equipped with balanced (XLR) type jacks. Wiring diagrams for these jacks are shown on “INPUT/OUTPUT Connector” of
“Connector Information”(p. 25). Make connections after first checking the wiring diagrams of other equipment you intend to connect.
Keyboard
Microphone
Powered speaker
Power amp
Speaker
Connecting Input Devices
Connect microphones and keyboards to INPUT 1 through 24.
Use male XLR connectors to make the connections.
* When connection cables with resistors are used, the volume
level of equipment connected to the inputs (INPUT 1–24) may
be low. If this happens, use connection cables that do not
contain resistors.
* When connecting equipment that has unbalanced output,
actual volume is lower than the volume level set using the
preamp on the S-2416 (This is not a malfunction).
MEMO
•
You can 48 V phantom power from the XLR connectors
at INPUT 1 through 24. When a condenser microphone or the
like is connected and supplying phantom power is required,
switch it on by remote control. Refer to “Making Settings for the
•
Preamp gain and phantom power on/off settings made by
remote control remain in memory after the power to the S-2416
is switched off. You can ensure that the settings are stored in
memory by locking the remote control before switching off the
power.
(Example) If you’re using the S-4000R:
Press the [LOCK] button to make it light up, wait several seconds,
then power off the S-2416.
Connecting Output Devices
Connect amps and powered speakers to OUTPUT 1 through 16.
OUTPUT 1 through 16 on the S-2416 are male connectors. Use
female XLR connectors to make the connections.
The signal level that is output is +4 dBu (nominal, maximum output:
+22 dBu).
If the input to the connected amps or powered speakers is too high
and the audio output is distorted, adjust the gain using the input
attenuator for the amp.
* Acoustic feedback could be produced depending on the
location of microphones relative to speakers. This can be
remedied by:
•
Changing the orientation of the microphone(s).
•
Relocating microphone(s) at a greater distance from speakers.
•
Lowering volume levels.


























