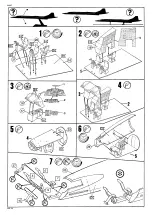
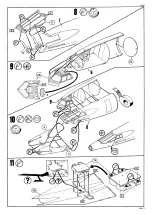
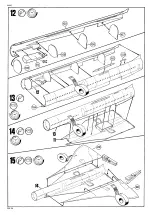
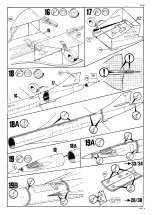
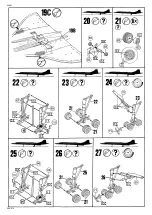
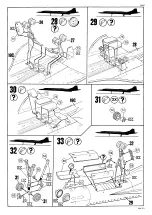
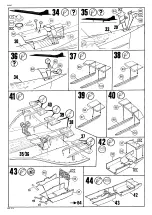
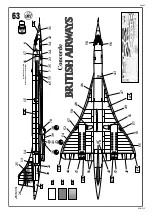
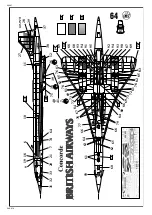
Concorde
British Airways
©2015 BY REVELL GmbH. A subsidiary of Hobbico, Inc.
04997-0389
PRINTED IN GERMANY
Concorde British Airways
Concorde British Airways
Beim Deltafl ügler Concorde von Aérospatiale-BAC handelt es sich um ein überschallschnelles
Passagierfl ugzeug, das von vier Turbojet-Triebwerken der Marke Rolls-Royce/Snecma Olym-
pus 593 angetrieben wurde (einer Weiterentwicklung der Triebwerke, die beim Bomber
Avro Vulcan der RAF verwendet wurden). Die Concorde wurde als Gemeinschaftsprojekt
von Aérospatiale und der British Aircraft Corporation (BAC) auf der Basis eines staatlichen
Abkommens zwischen Frankreich und Großbritannien entwickelt und produziert. Das Consor-
tium sicherte sich von 16 damaligen großen Fluglinien unverbindliche Bestellungen für über
100 Flugzeuge des Typs Concorde; mit jeweils sechs Maschinen waren Pan Am, BOAC und Air
France Erstbesteller. In den Auftragsbüchern standen weitere Fluglinien wie Panair do Brasil,
Continental Airlines, Japan Airlines, die Lufthansa, American Airlines, United Airlines, Air India,
Air Canada, Braniff, Singapore Airlines, Iran Air, Olympic Airways, Qantas, CAAC, Middle East
Airlines und TWA. Der Erstfl ug der Concorde fand im Jahr 1969 statt, in Jahr 1976 wurde sie
in Dienst gestellt und für einen Zeitraum von 27 Jahren als Verkehrsfl ugzeug genutzt. Letzten
Endes wurden jedoch nur 20 Flugzeuge des Typs in Frankreich und Großbritannien gebaut,
davon sechs als Prototypen und Versuchsmaschinen. Jeweils sieben Stück wurden an die Flug-
linien Air France und British Airways ausgeliefert, zu einem Verkaufspreis von einem franzö-
sischen Franc bzw. einem britischen Pfund pro Flugzeug. Die Concorde fl og u. a. regelmäßig
die Transatlantikroute von den Flughäfen London-Heathrow und Paris-Charles-de-Gaulle nach
New York-JFK, Washington-Dulles und Barbados, wobei sie die Flugzeit der herkömmlichen
Verkehrsfl ugzeuge auf diesen Strecken um mehr als die Hälfte unterbot. Die absenkbare
Nasenpartie der Concorde ermöglichte den Wechsel zwischen einer gestreckten Position, die
einen geringeren Luftwiderstand bot und eine optimale aerodynamische Effi zienz sicherte,
und ungehinderter Sicht für die Piloten während Start, Landung und dem Manövrieren auf
dem Rollfeld. Aufgrund des steilen Anstellwinkels hätte die lange spitze Nasenpartie ohne die-
se Maßnahme die Sicht behindert. Die absenkbare Nase wurde durch ein bewegliches Visier
ergänzt, das vor dem Absenkvorgang heruntergefahren wurde. Wurde die Nase waagerecht
ausgerichtet, hob sich das Visier vor die Frontscheibe des Cockpits, um so zu einer verbesserten
Aerodynamik beizutragen. Im Jahr 2003 wurde die Concorde außer Dienst gestellt, nachdem
sich die Luftfahrtindustrie nach dem einzigen Absturz des Typs am 25. Juli 2000, den Terror-
angriffen vom 11. September 2001 und der Entscheidung von Airbus, die Wartungsleistungen
einzustellen, in einem allgemeinen Abschwung befand. Virgin Atlantic wollte die Concorde-
Flotte der BA zu deren Einkaufspreis abkaufen, d. h. für ein britisches Pfund pro Stück, aber das
Angebot wurde von BA abgelehnt …
Einsatztyp Überschall-Verkehrsfl ugzeug
Hersteller BAC (nun BAE Systems) & Sud Aviation (später Aérospatiale und EADS)
Erstfl ug 2. März 1969
Indienststellung 21. Januar 1976
Außerdienststellung 26. November 2003
Status Außer Dienst gestellt
Hauptnutzer British Airways & Air France
Produktionszeitraum 1965 bis 1979
Gebaute Stückzahl 20 (davon 6 nicht durch Fluglinien genutzt)
Programmkosten 1,3 Mrd. Pfund
Herstellungskosten Flugz. 23 Mio. Pfund im Jahr 1977 (entspräche im Jahr 2014 einer Summe
von 125 Mio. Pfund bzw. 155.925.000
€
)
Allgemeine technische Daten:
Besatzung 3 Personen (2 Piloten und ein Bordingenieur)
Kapazität 92 bis 120 Passagiere
Länge 61,66 m
Tragfl ächenspannweite 25,6 m
Höhe 12,2 m
Innenlänge des Rumpfs 39,32 m
Innenbreitr des Rumpfs, max. 2,62 m
Innenhöhe des Rumpfs, max. 1,96 m
Leergewicht 78.700 kg
Nutzlast 111.130 kg
Treibstoffzuladung, max. 95.680 kg
Triebwerke 4 x Rolls-Royce/SNECMA Olympus 593 Mk 610 Strahltriebwerke mit Nachbrenner
Leistungsdaten:
Höchstgeschwindigkeit Mach 2,04 (2.179 km/h) auf Reisehöhe
Reisegeschwindigkeit Mach 2,02 (2.158 km/h) auf Reisehöhe
Reichweite 7.222,8 km
Dienstgipfelhöhe 18.300 m
Aérospatiale-BAC Concorde is delta-winged supersonic passenger airliner, turbojet-powered
with four Rolls-Royce/Snecma Olympus 593 engines based on those employed in the RAF‘s
Avro Vulcan bomber. Concorde was jointly developed and produced by Aérospatiale and
the British Aircraft Corporation (BAC) under an Anglo-French treaty. The consortium secured
non-binding orders for over 100 Concordes from 16 major airlines of the day: Pan Am, BOAC,
and Air France were the launch customers, with six Concordes each. Other airlines in the order
book included Panair do Brasil, Continental Airlines, Japan Airlines, Lufthansa, American Air-
lines, United Airlines, Air India, Air Canada, Braniff, Singapore Airlines, Iran Air, Olympic Airways,
Qantas, CAAC, Middle East Airlines, and TWA. First fl own in 1969, Concorde entered service
in 1976 and continued commercial fl ights for 27 years. In the end, only a total of 20 aircraft
were built in France and the United Kingdom; six of these were prototypes and development
aircraft. Seven each were delivered to Air France and British Airways, which were sold to the
airliners at 1 French Franc and 1 British Pound per aircraft. Among other destinations, Concorde
fl ew regular transatlantic fl ights from London Heathrow and Paris-Charles de Gaulle Airport
to New York JFK, Washington Dulles and Barbados; it fl ew these routes in less than half the
time of other airliners. Concorde‘s drooping nose enabled the aircraft to switch between being
streamlined to reduce drag and achieve optimum aerodynamic effi ciency, and not obstructing
the pilot‘s view during taxi, takeoff, and landing operations. Due to the high angle of attack,
the long pointed nose obstructed the view and necessitated the capability to droop. The droop
nose was accompanied by a moving visor that retracted into the nose prior to being lowered.
When the nose was raised to horizontal, the visor would rise in front of the cockpit windscreen
for aerodynamic streamlining. Concorde was retired in 2003 due to a general downturn in the
aviation industry after the type‘s only crash on 25 July 2000, the 9/11 terrorist attacks in 2001,
and a decision by Airbus to discontinue maintenance support. Virgin Atlantic wanted to buy
the Concorde fl eet from BA at the price they paid for it, being 1 Pound per aircraft, but this
proposal was rejected by BA...
Role Supersonic airliner
Manufacturer BAC (now BAE Systems) & Sud Aviation (later Aérospatiale and EADS)
First fl ight 2 March 1969
Introduction 21 January 1976
Retired 26 November 2003
Status Retired from service
Primary users British Airways & Air France
Produced 1965 to 1979
Number built 20 (including 6 non-airline aircraft)
Program cost 1.3 billion Pounds
Aircraft cost 23 million Pounds in 1977 (125 million in 2014 pounds)
General characteristics:
Crew: 3 (2 Pilots and a fl ight engineer)
Capacity: 92 / 120 passengers
Length: 61.66 m
Wingspan: 25.6 m
Height: 12.2 m
Fuselage internal length: 39.32 m
Fuselage width: maximum of 2.62
internal Fuselage height: maximum of 1.96 m
internal Empty weight: 78,700 kg
Useful load: 111,130 kg Maximum
fuel load: 95,680 kg
Powerplant: 4x Rolls-Royce/SNECMA Olympus 593 Mk 610 afterburning turbojets
Performance:
Maximum speed: Mach 2.04 (2,179 km/h) at cruise altitude
Cruise speed: Mach 2.02 (2,158 km/h) at cruise altitude
Range: 7,222.8 km
Service ceiling: 18,300 m
Содержание Concorde British Airways
Страница 2: ...04997 PAGE 2 ...
Страница 6: ...04997 PAGE 6 ...
Страница 7: ...04997 PAGE 7 ...
Страница 8: ...04997 PAGE 8 ...
Страница 9: ...04997 PAGE 9 ...
Страница 10: ...04997 PAGE 10 ...
Страница 11: ...04997 PAGE 11 ...
Страница 12: ...04997 PAGE 12 ...
Страница 13: ...04997 PAGE 13 ...
Страница 14: ...04997 PAGE 14 ...