NB-IoT
Module Series
BC660K-GL Hardware Design
BC660K-GL_Hardware_Design 29 / 57
according to the actual situation.
MAIN_TXD
MAIN_RXD
RI
Module
GND
C1+
C1-
C2+
C2-
V+
VCC
GND
V-
3.3 V
T1IN
T2IN
T3IN
T4IN
R1IN
R2IN
R3IN
R1OUT
R2OUT
R3OUT
T1OUT
T2OUT
T5OUT
T3OUT
T4OUT
T5IN
GND
GND
R1OUT
1
2
3
4
5
7
8
9
GND
To PC Main Serial Port
GND
RS-232
Transceiver
6
VIO_SEL
0
Ω
R1
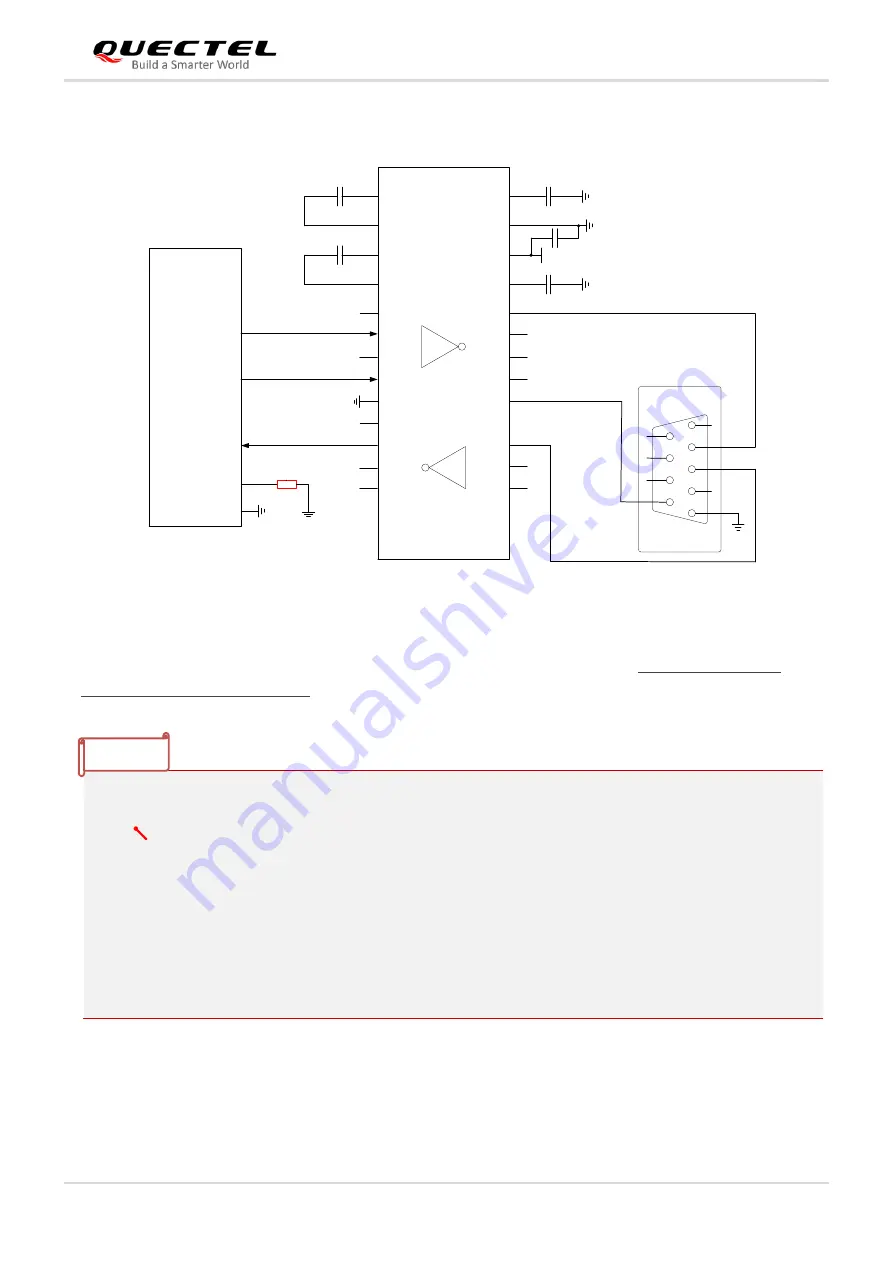
Figure 14: Reference Design for Module-PC Communication via RS-232 Interface
Please visit vendors
’ websites to select a suitable RS-232 transceiver, such as http://www.exar.com and
http://www.maximintegrated.com.
1. If the voltage domain of your application system is 1.8 V, keep the R1 in
red
not mounted; if it is
3.3 V, keep the R1 in
red
mounted.
2.
“
” represents the test points of UART interfaces. It is recommended to reserve the test points of
VBAT, BOOT and RESET_N for convenient firmware upgrade and debugging when necessary.
3. MAIN_RXD cannot be pulled up to VDD_EXT directly. To pull up MAIN_RXD to VDD_EXT, you
need to connect a Schottky diode in series first, and then add a pull-up resistor of 4.7
–20 kΩ. For
more details, see
document [3]
.
4.
1)
When VIO_SEL is grounded and VBAT
˂
3.3 V, VDD_EXT = VBAT;
When VIO_SEL is grounded and
VBAT ≥ 3.3 V, VDD_EXT = 3.3 V;
When VIO_SEL is floating, VDD_EXT = 1.8 V.
When the serial port voltage is neither 1.8 V nor 3.3 V, it is recommended to use a level conversion circuit.
For the design of the circuit shown in the dotted line, refer to that shown in the solid lines, and pay
attention to the connection direction. In this case, the design of RI
– GPIO circuit can refer to that of the
MAIN_TXD
– RXD circuit.
NOTES
















































