G.SHDSL .bis Router User Manual V0.04
30
The table displays IP addresses and MAC added to the Static DHCP list.
Click on Apply to save the parameters or Cancel to start configuring this page from beginning.
4
4
.
.
3
3
.
.
6
6
V
V
L
L
A
A
N
N
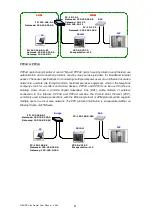
VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) allows a physical network to be partitioned into multiple logical
networks. Devices on a logical network belong to one group. A device can belong to more than
one group. With VLAN, a device cannot directly talk to or hear from devices that are not in the
same group.
With MTU (Multi-Tenant Unit) applications, VLAN is vital in providing isolation and security among
the subscribers. When properly configured, VLAN prevents one subscriber from accessing the
network resources of another on the same LAN.
VLAN also increases network performance by limiting broadcasts to a smaller and more
manageable logical broadcast domain. In traditional switched environments, all broadcast packets
go to each every individual port. With VLAN, all broadcasts are confined to a specific broadcast
domain.
The IEEE 802.1Q defines the operation of VLAN bridges that permit the definition, operation, and
administration of VLAN topologies within a bridged LAN infrastructure.
The router supports two types of VLAN:
802.1Q Tag-Based VLAN
and
Port-Based VLAN
.
VID: (Virtual LAN ID) It is an definite number of ID range from 1 to 4094.
PVID: (Port VID) It is an untagged member from 1 to 4094 of default VLAN.
ADVANCED>VLAN