Appendix B
Wi-Fi Encryption & Authentication
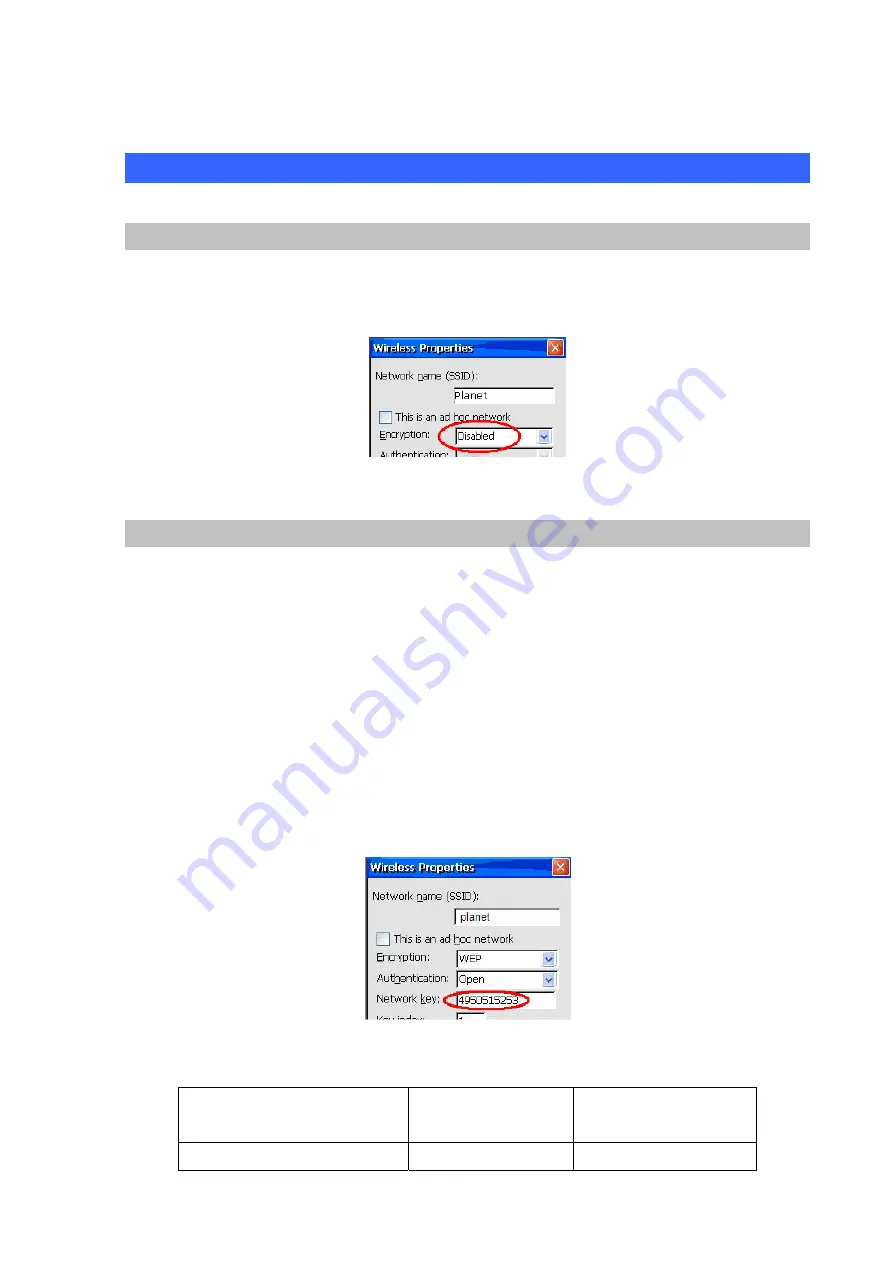
No Encryption
If you are connecting to an AP that requires no encryption or authentication, you can leave the
Encryption setting in the Wireless Properties screen to “Disabled”, and press Connect, just as shown
below:
Figure 202. Encryption disable
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is a scheme to secure data transmission over WiFi networks. WEP
relies on a secret key that is shared between a mobile station and an access point. The secret key is
used to encrypt packets before they are transmitted, and an integrity check is used to ensure that
packets are not modified in transit. For the WEP key, you need to supply a 64 or 128 bit key, which is
usually a string of 5 or 13 characters. However, this string will differ depending on whether the AP has
been configured to accept an ASCII or hexadecimal key. Most of the commercial APs have been
configured to accept a hexadecimal key, i.e. a string made up of characters from 0-9 and A-F. So if the
AP require a hexadecimal key “12345”, you can just enter “12345” at your WLAN phone. However, if
the AP requires you to enter an ASCII key of “12345”, you need to enter “4950515253” as your key,
(since 49 is the ASCII value of 1, and 50 is the ASCII value of 2, and 51 is that of 3, and so on), as
shown below:
Figure 203. Wep setting
The following table will provide another example of such differences (assuming the key is “ABCDE”):
115
AP with 64 bit ASCII
key
AP with 64 bit
hexadecimal key
Key to be entered at the phone
65
66
67
68
69
ABCDE
















































