192-011006N8 PSD1 Installation Guide
192-011006N8 2019-07
09.10.19 09:27
69 (109)
6.1.4.
Advantages of using the "safe torque off" safety function" STO
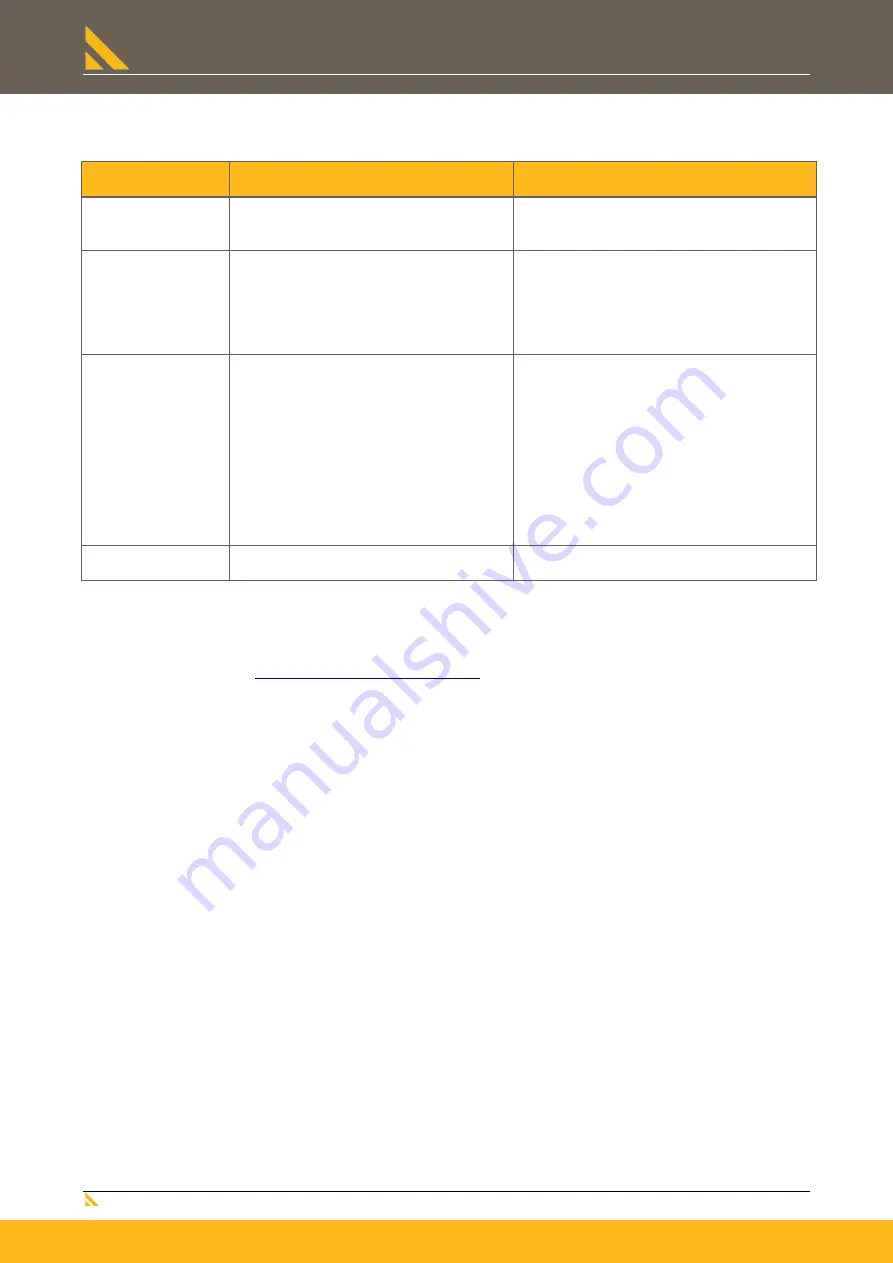
Safety category 3 in accordance with EN ISO 13849-1
Requirements
performance features
Use of the safe torque off function
Conventional solution: Use of external
switching elements
Reduced switching
overhead
Simple wiring, certified application examples
Grouping of drive controllers on a mains
contactor is possible.
Two safety-oriented power contactors in series
connection are required.
Use in the production
process
High operating cycles,
high reliability, low
wear
Extremely high operating cycles thanks to
almost wear-free technology (low-voltage
relay and electronic switch). The "safe torque
off" status is attained due to the use of
wear-free electronic switches (IGBTs).
This performance feature cannot be reached
with conventional technology.
Use in the production
process
High reaction speed,
fast restart
Drive controller remains performance- and
control-oriented in connected state.
No significant waiting times due to restart.
When using power contactors in the supply, a
long waiting time for the energy discharge of the
DC link circuit is required.
When using two power contactors on the motor
side, the reaction times may increase, you must
however take into consideration other
disadvantages:
a) Securing that switching takes only place in
powerless state (Direct current! Constant
electric arcs must be prevented).
b) Increased overhead for EMC conform wiring.
Emergency-stop
function
Allowed
Allowed
6.2
STO Operating Principle
In this chapter you can read about:
•
STO principle with PSD1-S ....................................................................................................... 70
•
STO principle of PSD1-S with one axis module ........................................................................ 70
•
STO principle of PSD1-M with two axis modules ...................................................................... 70
•
STO principle of PSD1-M with three axis modules .................................................................... 71
Principle
The current flow in the motor windings is controlled by a power semiconductor
bridge (6-fold IGBT).
A rotating field is created via the processor by means of the power output stage.
Between control logic and power module, optocouplers are used for potential
separation.
The STO input are on the front panel. 2 optocouplers are controlled via 2 STO
channels (STOA/ & STOB/). At a STO via external safety control both auxiliary
power supplies of the power output stage are switched off via 2 channels. Due to
this fact the power semiconductor bridge is blocked and there is no motor current.
The reset procedure of the Safe Torque Off depends on the configurated settings
of the object STO_Setup.
At standard settings STO_Setup=0 the motor may be powered as soon as STOA/
and STOB/ inputs are reset to high level.
At settings STO_Setup=1 the generated error 0x5492 needs be acknowledged
before the motor can be powered again.
Detection of hardware failure
An internal Hardware monitoring recognizes the failure of the optocoupler by
continuously comparing both channels. If the monitoring system recognizes a
discrepancy for a defined time (approx. 10 s) the fault is stored in the hardware.
This is reported via the error code 0x5493 ?.
The error can only be reset by a hardware reset (switching off and on the servo
drive). But before the error must be found and solved by the user.






























