SmartNA-X 1G/10G Modular | Restricting Traffic with Filters |
55
SmartNA-X
™
1G/10G User Guide 1.4
©
2015 Network Critical Solutions Limited
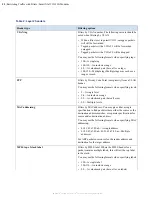
Header type
Filtering options
• 0/1—A value/mask pair (here: all even types)
• 10,12,14—Multiple types (use commas to separate
values, no spaces). Types may each use a range or
mask.
ICMPcode
Filter by ICMP code when filtering by ICMP packet
(protocol number 1). The following formats are recognised:
• 10—A single code
• 10–14—An inclusive range
• 0/1—A value/mask pair (here: all even codes)
• 10,12,14—Multiple codes (use commas to separate
values, no spaces). Codes may each use a range or
mask.
Defining custom fields
You can use custom fields to filter on user-defined bytes (UDBs) in a packet header. The positioning of the custom field
within the packet is done by specifying an anchor and an offset value. The custom field itself can be up to 32 bits long.
Custom fields are applied by defining a filter of the same packet type, and specifying the custom field and UDBs that you
want to apply to the filter.
The following limitations apply for custom fields:
• No more than two underlying user-defined bytes anchored on start-of-packet can be used at once.
• No more than three underlying user-defined bytes can be used in conjunction with other filtering on IPv6 headers for
traffic from the same ingress port.
• No more than six underlying user-defined bytes can be used in total at any given time.
Here, "used" refers to custom fields that can actually affect passing traffic. Other custom fields may still be defined, and
filters may be defined using them, but these don't count toward the totals as long as the filters aren't applied to any maps.
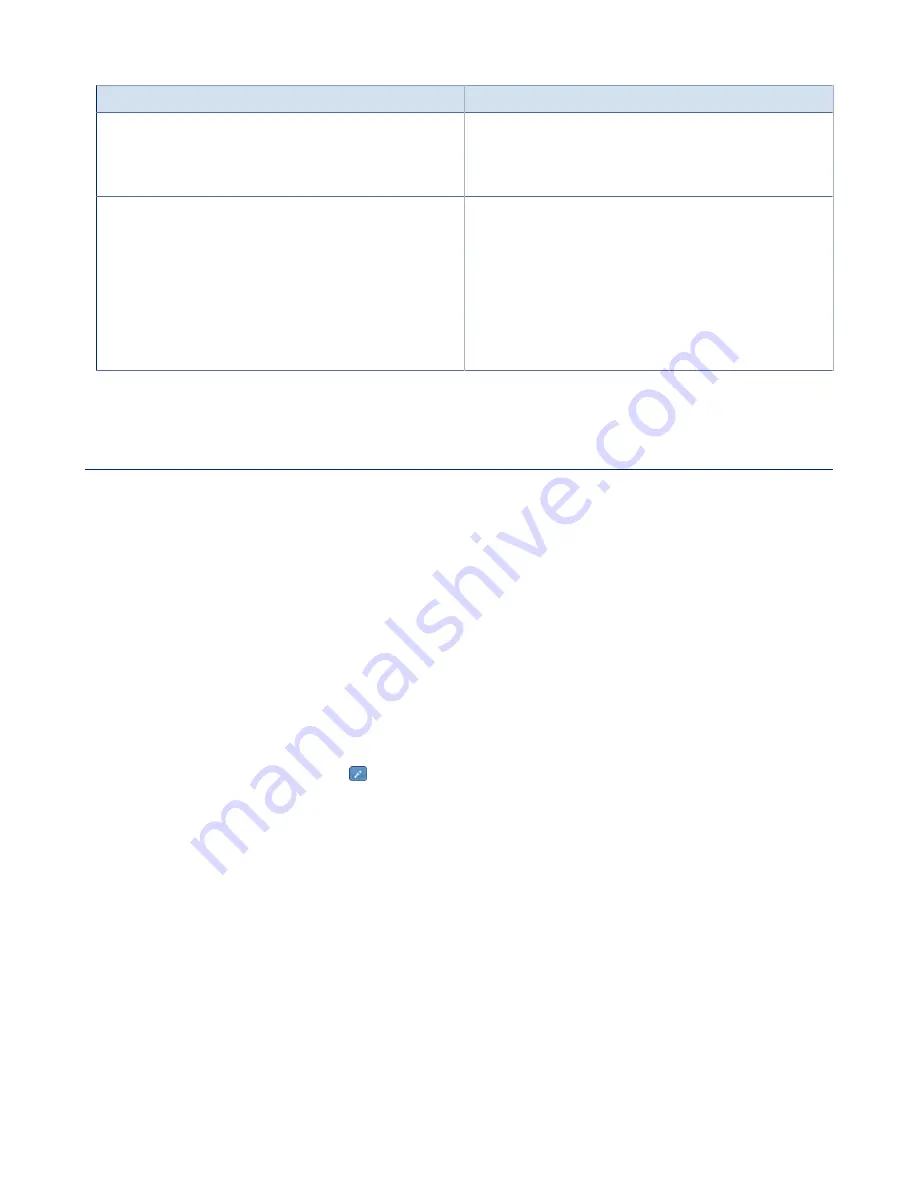
1.
Click on the chassis and select the
Custom fields
tab.
2.
Click
Add new custom field
, or click to edit an existing custom field.
3.
Enter a unique name for the custom field. This name will be available in the Custom fields section in the filter
definition screen if the packet type you choose when defining the filter is compatible with the scope of any custom
fields you've defined.
4.
Enter details for the custom field:
•
Scope
—Select what types of filters may use the custom field, either all, all IP, IPv4, IPv6, ARP, or MPLS filters.
•
Anchor
—Select the starting position of the custom field in the packet, either at the start of the packet, at the start
of the layer 3 header, at the start of the layer 4 header, or at the start of the IPv6 extension header.
•
Offset
—Enter an offset position relative to the anchor position for the start of the field. You may enter offset
values of 0–1007 bits.
•
Length
—Enter a length for the field. The field length can be 1–32 bits. The offset plus the length of the field must
not exceed 1008 bits.
5.
Click
Add custom field
to finish defining the custom field.
6.
Click
Review/apply
and review pending changes. To apply these changes to the system, click
Apply changes
or click
'
X
' to cancel.