52
| Restricting Traffic with Filters | SmartNA-X 1G/10G Modular
SmartNA-X
™
1G/10G User Guide 1.4
©
2015 Network Critical Solutions Limited
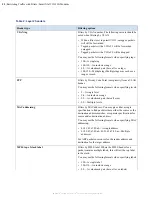
Table 2: Layer 2 headers
Header type
Filtering options
VLAN tag
Filters by VLAN number. The following caveats should be
noted when filtering by VLAN:
• When a filter is set to permit VID 1, untagged packets
will still be forwarded.
• Tagged packets with a VID of 1 will be forwarded
untagged.
• Tagged packets with a VID of 0 will be dropped.
You may use the following formats when specifying tags:
• 100—A single tag
• 100-110—An inclusive range
• 0/1—A value/mask pair (here: all even tags)
• 100, 150—Multiple tags Multiple tags may each use a
range or mask.
PCP
Filters by Priority Code Point (user priority) from a VLAN
header.
You may use the following formats when specifying levels:
• 2—A single level
• 2-4—An inclusive range
• 0/1—A value/mask pair (here all even)
• 0,2—Multiple levels
MAC addressing
Filters by MAC address. You may give either a single
specification to find packets where either the source or the
destination address matches, or separate specifications for
source and/or destination address.
You may use the following formats when specifying MAC
addressing:
• 01:23:45:67:89:ab—A single address
• 01:23:45:67:89:ab, 01:23:45:67:89:ac—Multiple
addresses
For ARP packets use source for the sender address and
destination for the target address.
MPLS top of stack label
Filters by MPLS label. Where the MPLS header for a
packet contains multiple labels, this will test the top label
in the stack.
You may use the following formats when specifying labels:
• 100—A single label
• 100-110—An inclusive range
• 0/1—A value/mask pair (here: all even labels)