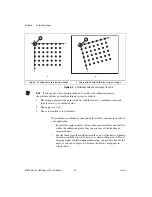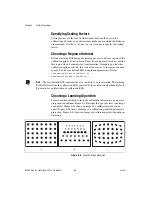
Chapter 5
Performing Machine Vision Tasks
IMAQ Vision for LabWindows/CVI User Manual
5-26
ni.com
6.
Test the color location algorithm on test images using
imaqMatchColorPattern()
.
7.
Verify the results using a ranking method.
You can save the template image using
imaqWriteVisionFile()
.
Convert Pixel Coordinates to Real-World Coordinates
The measurement points you located with edge detection and pattern
matching are in pixel coordinates. If you need to make measurements using
real-world units, use
imaqTransformPixelToRealWorld()
to convert
the pixel coordinates into real-world units.
Make Measurements
You can make different types of measurements either directly from the
image or from points that you detect in the image.
Distance Measurements
Use the following functions to make distance measurements for your
inspection application.
Clamp functions measure the separation between two edges in a
rectangular search region. First, clamp functions detect points along
the two edges using the Rake function. Then, they compute the distance
between the points detected on the edges along each search line of the
rake and return the largest or smallest distance. The
imaqSelectRect()
function generates a valid input search region for these functions. You also
need to specify the parameters for edge detection and the separation
between the search lines that you want to use within the search region
to find the edges. These functions work directly on the image under
inspection, and they output the coordinates of all the edge points that
they find. The following list describes the available clamp functions:
•
imaqClampMax()
—Measures the largest separation between
two edges in a rectangular search region.
•
imaqClampMin()
—Finds the smallest separation between two
edges.
Use
imaqGetDistance()
to compute the distances between two points,
such as consecutive pairs of points in an array of points. You can obtain
these points from the image using any one of the feature detection methods
described in the
section of this chapter.