© National Instruments
|
2-3
NI cDAQ-9132/9133/9134/9135/9136/9137 User Manual
Scanned Modules
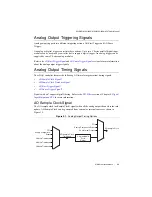
Scanned C Series analog input modules contain a single ADC and a multiplexer to select
between multiple input channels. When the cDAQ Module Interface receives a Sample Clock
pulse, it begins generating a Convert Clock for each scanned module in the current task. Each
Convert Clock signals the acquisition of a single channel from that module. The Convert Clock
rate depends on the module being used, the number of channels used on that module, and the
system Sample Clock rate.
The driver chooses the fastest conversion rate possible based on the speed of the ADC for each
module and adds 10 μs of padding between each channel to allow for adequate settling time. This
scheme enables the channels to approximate simultaneous sampling. If the AI Sample Clock rate
is too fast to allow for 10 μs of padding, NI-DAQmx selects a conversion rate that spaces the
AI Convert Clock pulses evenly throughout the sample. NI-DAQmx uses the same amount of
padding for all the modules in the task. To explicitly specify the conversion rate, use the
ActiveDevs
and
AI Convert Clock Rate
properties using the
DAQmx Timing
property node
or functions.
Simultaneous Sample-and-Hold Modules
Simultaneous sample-and-hold (SSH) C Series analog input modules contain multiple ADCs or
circuitry that allows all the input channels to be sampled at the same time. These modules sample
their inputs on every Sample Clock pulse.
Sigma-Delta Modules
Sigma-delta C Series analog input modules function much like SSH modules, but use ADCs that
require a high-frequency oversample clock to produce accurate, synchronized data. Some
sigma-delta modules in the cDAQ controller automatically share a single oversample clock to
synchronize data from all the modules that support an external oversample clock timebase when
they all share the same task. (DSA modules are an example). The cDAQ controller supports a
maximum of two synchronization pulse signals configured for your system. This limits the
system to two tasks with different oversample clock timebases.
The oversample clock is used as the AI Sample Clock Timebase. While most modules supply a
common oversample clock frequency (12.8 MHz), some modules, such as the NI 9234, supply
a different frequency. When sigma-delta modules with different oversample clock frequencies
are used in an analog input task, the AI Sample Clock Timebase can use any of the available
frequencies; by default, the fastest available is used. The sampling rate of all modules in the
system is an integer divisor of the frequency of the AI Sample Clock Timebase.
When one or more sigma-delta modules are in an analog input task, the sigma-delta modules also
provide the signal used as the AI Sample Clock. This signal is used to cause analog-to-digital
conversion for other modules in the system, just as the AI Sample Clock does when a
sigma-delta module is not being used.
When sigma-delta modules are in an AI task, the controller automatically issues a
synchronization pulse to each sigma-delta module that resets their ADCs at the same time.