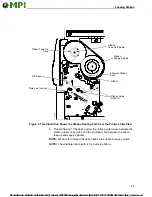
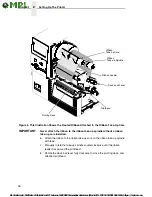
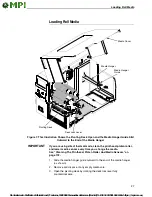
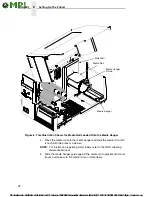
14
1
Thermal Printer Technology
•
Ethernet Interface Card:
Allows you to attach the printer to a LAN (Local
Area Network) rather than attaching it directly to a host computer. The
Printer Management Utility (PMU) remote management software is
standard with this option.
Ethernet adapters are available as user installable option, mounted inside
the printer with the 10/100Base-T (UTP) connection only.
•
Ethernet, Wireless:
Provides wireless 802.11b/g connectivity without
expensive cabling and reconfigurations required from a wired network.
PMU is standard with this option.
•
Real Time Clock:
A clock chip with internal battery that keeps track of the
year, month, day, hour, minute, and second values. It continues to
operate when the printer is off.
•
RFID Encoder:
The RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) encoder
programs smart labels (tags with embedded inlays).
•
Standard Peel with Liner Rewinder:
In Label Peel-Off mode, peels off
labels one at a time before printing the next label and rewinds the liner
into a discardable roll.
•
Standard Peel without Liner Rewinder:
The Peel-Off mode peels labels
while discarding the dispensed liner in front of the printer.
For more information about printer options, see Appendix B on page 221.
Thermal Printer Technology
Quiet and fast, with excellent print quality, your multifunction thermal printer
uses an inline thermal printhead. The thermal printer operates differently from
a line matrix or laser printer, because the thermal printer uses a printhead with
heating elements and special paper or ribbon.
The Printing Process
The thermal printhead allows two modes of operation:
•
Direct Thermal
During
direct
thermal printing, the thermal printhead selectively heats
small, rectangular
thermal
dots.
When these contact the coated thermal
paper, the dyes and developers in the coating react to the heat and
develop an image. This mode of printing is generally used for short-term
labeling applications.
•
Thermal Transfer
During thermal
transfer
printing, the heated thermal dots contact a
thermal ribbon. The heat reacts with the ribbon and bonds the image to
the paper. This method is used especially for abrasive, long-storage
applications and for specialized applications, such as in extreme
environmental conditions or where tamper-proofing is required.