UC-7400-LX Plus User’s Manual
Managing Communications
4-9
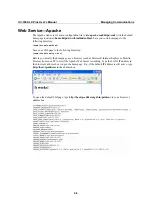
NAT Example
The IP address of LAN1 is changed to 192.168.3.127 (you will need to load the module
ipt_MASQUERADE):
Embedded Computer
PC1 (Linux or Windows)
IP/Netmask:
Gateway:
192.168.3.100/24
192.168.3.127
PC2 (Linux or Windows)
IP/Netmask:
Gateway:
192.168.4.100/24
192.168.4.127
LAN1
LAN2
LAN1: 192.168.3.127/24
LAN2: 192.168.4.127/24
NAT Area / Private IP
1.
#echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
2.
#modprobe ip_tables
3.
#modprobe ip_conntrack
4.
#modprobe iptable_nat
5.
#modprobe ipt_MASQUERADE
6.
#iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE
Enabling NAT at Bootup
In most real world situations, you will want to use a simple shell script to enable NAT when the
UC-7400-LX Plus boots up. The following script is an example.
#!/bin/bash
# If you put this shell script in the /home/nat.sh
# Remember to chmod 744 /home/nat.sh
# Edit the rc.local file to make this shell startup automatically.
# vi /etc/rc.d/rc.local
# Add a line in the end of rc.local /home/nat.sh
EXIF=‘eth0’ #This is an external interface for setting up a valid IP address.
EXNET=‘192.168.4.0/24’ #This is an internal network address.
# Step 1. Insert modules.
# Here 2> /dev/null means the standard error messages will be dump to null device.
modprobe ip_tables 2> /dev/null
modprobe ip_conntrack 2> /dev/null
modprobe ip_conntrack_ftp 2> /dev/null
modprobe ip_conntrack_irc 2> /dev/null
modprobe iptable_nat 2> /dev/null
modprobe ip_nat_ftp 2> /dev/null
modprobe ip_nat_irc 2> /dev/null
# Step 2. Define variables, enable routing and erase default rules.
PATH=/bin:/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/local/sbin