6 - 8
MC9190-G Integrator Guide
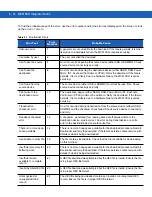
Volatile File Storage (Cache Disk)
Windows Mobile 6.5 memory architecture uses persistent storage for all files, registry settings, and database
objects to ensure data is retained even after a power failure. Persistent storage is implemented using Flash
memory technology which is generally slower than volatile RAM memory. In certain situations the speed of the
operation is more important than the integrity of the data. For these situations, Motorola has provided a small
volatile File Storage volume, accessed as the
Cache Disk
folder. Disk operations to the
Cache Disk
folder are
much faster than to any of the persistent storage volumes, but data is lost across warm boots and power
interruptions. Note that a backup battery powers RAM memory, including the
Cache Disk
, when you remove the
main battery for a short period of time.
The MC9190-G uses the
Cache Disk
for temporary data that can be restored from other sources, for example, for
temporarily “caching” HTML web pages by a browser or generating formatted files to send to a printer. Both
situations benefit from the increased speed of the cache disk, but you can restore the data if needed.
DO NOT use the
Cache Disk
as a method to improve application performance. Analyze applications that perform
slower in persistent storage to optimize disk access. Common areas for optimization include minimizing the
number of reads and writes to a file, removing unneeded debug logging, and minimizing file flushing or closing
files.
Persistent Storage
Windows Mobile 6.5 protects all data and applications from power-related loss. Because Windows Mobile 6.5
mounts the entire file system and registry in persistent storage (rather than using RAM), MC9190-G devices
provide a reliable storage platform even in the absence of battery power.
Persistent storage provides application developers with a reliable storage system available through the standard
file system and registry APIs. Persistent storage is optimized for large reads and writes; therefore, applications
reading and writing data in large chunks tend to outperform those applications reading and writing small blocks of
data. Data in persistent storage is lost upon a clean boot.
Persistent storage contains all the directories under the root directory except for Application, Cache Disk, and
Storage Card (if a storage card is installed). Persistent storage is approximately 700 MB (formatted).
Application Folder
The Application folder is a super-persistent storage that is persistent even after a clean boot. Accessing data in the
Application folder is slower than accessing persistent storage. The Application folder is used for deployment and
device-unique data. For example, network profiles can be stored in the Application folder so that connection to the
network is available after a cold boot. The Application folder is approximately 117 MB (formatted).
Deployment
To install applications onto the MC9190-G, developers package the application and all required files into a CAB
file, then load the file onto the MC9190-G using one of the following options:
•
Microsoft ActiveSync 4.5 or higher
•
Storage Card
•
MSP 3.2
•
AirBEAM
•
Image Loader Image (for updating the operating system).
Содержание MC9190-G
Страница 1: ...MC9190 G Integrator Guide ...
Страница 2: ......
Страница 3: ...MC9190 G Integrator Guide 72E 140937 01 Rev A February 2011 ...
Страница 6: ...iv MC9190 G Integrator Guide ...
Страница 14: ...xii MC9190 G Integrator Guide ...
Страница 66: ...2 42 MC9190 G Integrator Guide ...
Страница 80: ...4 6 MC9190 G Integrator Guide ...
Страница 114: ...7 6 MC9190 G Integrator Guide ...
Страница 152: ...A 24 MC9190 G Integrator Guide ...
Страница 176: ...C 6 MC9190 G Integrator Guide ...
Страница 184: ...Glossary 8 MC9190 G Integrator Guide ...
Страница 189: ......