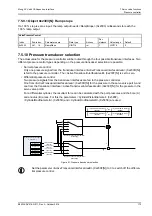
Moog ACV with CANopen bus interface
7 Servo valve functions
Pressure controller
B99224-DV018-D-211, Rev. A, October 2018
186
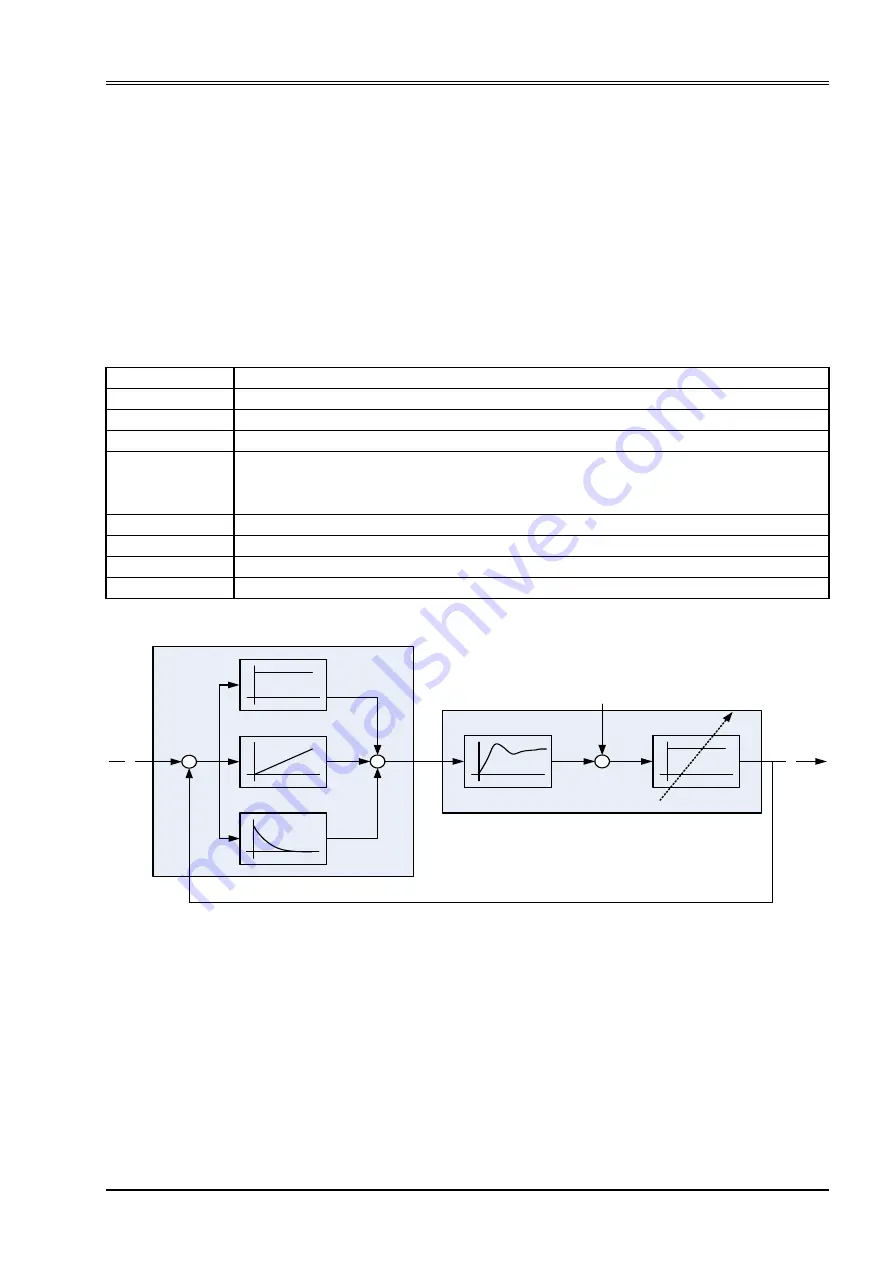
7.5.21 Automatic parameterization of the pressure controller
The tuning of the proportional, integral & differential gains (P-I-D) of the pressure controller is not straightfor-
ward. The automatic parameterization simplifies this by using only one gain value, namely the hydraulic ca-
pacitance. There are two preconditions that have to be considered. The automatic parameterization is possi-
ble for:
• Pressure control where the oil volume is nearly constant
• Small pressure control range
In this case a simple linear model of the plant can be used. The dynamic parameters of the linearized servo
valves are well known. Only the gain V
qu
of the servo valve depends on the actual pressure. This issue can be
solved by changing the hydraulic capacity, because this parameter influences the whole plant gain. Following
parameters are used in the model:
Figure 92: Parameterization of the pressure controller
An applicable way to find controller parameters for a stable system behavior is to use the 'worst case' pres-
sure setpoint value for controller tuning. The worst case pressure setpoint value is the highest required value.
The <SysPressureReference> (0x231C) must be set for the used pressure sensor interface. The
<HydraulicCapacity> (0x230C) should be increased slowly up till the pressure controller behavior becomes
unstable. Then it should be reduced until the controller becomes stable again. Setting the parameter
<HydraulicCapacity> (0x230C) to zero turns off the automatic parameter calculation.
Parameter name
Description
V
qu
Linear gain between setpoint value and flow (depends on working point)
D
v
Servo valve damping (depends on setpoint amplitude)
w
v
Servo valve natural frequency in [rad/s]
Hydraulic capacity C
H
[10
-6
l/bar] with:
V
Oil in the pipes volume [m
3
]
E
Oil
Compressibility module ~1.8*10
-9
[Pa]
K
P
Pressure controller proportional gain (calculation depends on C
H
)
K
I
Pressure controller integrator gain (calculation depends on C
H
)
K
D
Pressure controller differential gain (calculation depends on C
H
)
T
1
Pressure controller differential time constant (calculation depends on C
H
)
Table 84: Parameters used in a linear plant model
C
H
V
E
Oil
--------------
=
PID controller
Linear plant model
Ac
tu
al
v
al
u
e
Se
t v
alue
-
1/C
H
V
qu
, D
v
, w
v
K
D
, T
1
K
P
K
I