Autolab/Electronic load combination
20 |
P a g e
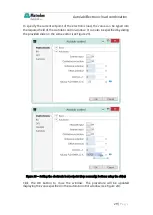
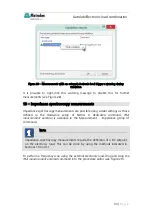
8.3
– Controlling the electronic load
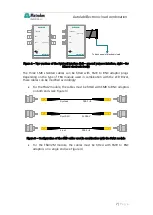
The control of the electronic load is achieved by providing an analog (0-10 V)
signal from the Dynload interface to the external programming connection of the
load.
The output of the Dynload interface in turn is controlled by the output of the
DAC164
1 of the Autolab and the FRA2/FRA32M V
output, if applicable.
The conversion settings depend on the type of load and are specified in the
software.
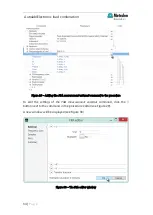
8.3.1
– Controlling the electronic load (TDI)
The TDI RBL 488 (100 V, 300 A, 2000 W) is an electronic load with a maximum
voltage of 100 V and a maximum current of 300 A.
If the load is in constant current (CC) mode, with the 300 A current range
selected, the conversion will be:
𝐶
𝑓
=
−
10
𝑉
300
𝐴
=
−
0.03333
𝑉
/
𝐴
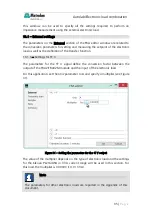
With a 0 V analog signal from the PGSTAT, the load will operate at 0 A. With a 10
V analog signal from the PGSTAT, the load will operate at 300 A.
The same conversion is used for the current readout. The electronic load has an
analog output corresponding to the measured current. The range of the current
monitor analog signal is 0-10 V, which corresponds to the range of 0 A to
maximum current, which depends on the selected current range of the electronic
load.
The TDI RBL 488 (100 V, 300 A, 2000 W) is an electronic load with a maximum
voltage of 100 V and a maximum current of 300 A. Operating in the 300 A current
range, the current monitor conversion factor will be:
𝐶
𝑓
=
−
300
𝐴
10
𝑉
=
−
30
𝐴
/
𝑉
With 0 V output voltage measured on the current monitor, the current drained by
the electronic load is 0 A. When 10 V output voltage is measured, the current
drained by the electronic load it the maximum value of 300 A.
8.3.2
– Controlling the electronic load (Kikusui)
The Kikusui PLZ164WA (150 V, 33 A, 165 W) is an electronic load with a
maximum voltage of 150 V and a maximum current of 33 A. The maximum power
is 165 W.