- 8 -
Most observers will want to have 3 or 4 eyepieces and perhaps
the #140 2x Barlow Lens to achieve the full range of reasonable
magnifications. See OPTIONAL ACCESSORIES, page 11, for
further details.
ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVING
The Starfinder telescope is an excellent observing tool for the
serious amateur astronomer. The range of observable
astronomical objects is, with minor qualification, limited only by
the observer's motivation.
This section provides a basic introduction to the terminology
associated with astronomy, and includes instructions for finding,
following and photographing celestial objects.
Celestial Coordinates:
Declination and Right Ascension
Celestial objects are mapped according to a coordinate system
on the Celestial Sphere, the imaginary sphere on which all stars
appear to be placed. This celestial object mapping system is
analogous to the Earth-based coordinate system of latitude and
longitude.
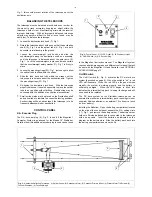
The poles of the celestial coordinate system are defined as
those two points where the Earth's rotational axis, if extended to
infinity, north and south, intersect the celestial sphere (Fig. 10).
Thus, the North Celestial Pole is that point in the sky where an
extension of the Earth's axis through the North Pole intersects
the celestial sphere. This point in the sky is located near the
North Star, Polaris.
In mapping the surface of the Earth, lines of longitude are drawn
between the North and South Poles. Similarly, lines of latitude
are drawn in an east-west direction, parallel to the Earth's
Equator. The Celestial Equator is a projection of the Earth's
Equator onto the celestial sphere.
(e.g., the Declination of the South Celestial Pole is -90°). See
Fig. 10. Any point on the celestial equator itself (which, for
example, passes through the constellations Orion, Virgo and
Aquarius) is specified as having a Declination of zero, shown as
0° 0' 0".
The celestial analog to Earth longitude is called "Right
Ascension", or "R.A.", and is measured in time on the 24 hour
"clock" and shown in hours ("hr"), minutes ("min") and seconds
("sec") from an arbitrarily defined "zero" line of Right Ascension
passing through the constellation Pegasus. Right Ascension
coordinates range from 0hr 0min 0sec to 23hr 59min 59sec.
Thus there are 24 primary lines of R.A., located at 15 degree
intervals along the celestial equator. Objects located further and
further east of the prime Right Ascension grid line (0hr 0min
0sec) carry increasing R.A. coordinates.
All celestial objects are specified in position by their celestial
coordinates of Right Ascension and Declination. T h e
telescope's Dec and R.A. setting circles (8) and (17), Fig. 1,
may be dialed to the coordinates of a specific celestial object,
which may then be located without a visual search. However,
before making use of the telescope's setting circles to locate
celestial objects, your telescope must first be polar aligned.
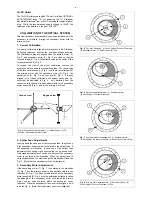
Polar Alignment
By polar aligning the telescope, two important telescope
capabilities are enabled: (a) the motor drive permits the
telescope to track any astronomical object, automatically; (b) the
telescope's Dec and R.A. setting circles, discussed above, may
be used to locate faint celestial objects directly from their
catalogued coordinates.
Celestial objects are essentially fixed on the celestial sphere;
however, they appear to move across the sky in an arc as the
Earth rotates on its axis, with a complete rotation of the Earth
occurring once in every 24 hour period. This apparent motion is
not obvious to the unaided eye, but viewed through a telescope
such as the Starfinder, this motion is rapid indeed. Objects
centered in the telescope move entirely out of the field of view
in 15 to 60 seconds, depending upon the magnification
employed.
During the 24 hour period of the Earth's rotation, stars make one
complete revolution about the Celestial Pole, making concentric
Fig. 10: The Celestial Sphere.
Fig. 11: Aligning the Telescope With the Celestial Pole. (1) Polar
Axis; (2) Polar Casting; (3) North-Pointing Leg.
3
1
2
Just as on the surface of the Earth, in mapping the celestial
sphere imaginary lines have been drawn to form a coordinate
grid. Thus, celestial object positions on the Earth's surface are
specified by their latitude and longitude. For example, Los
Angeles, California, can be located by its latitude (34°) and
longitude (118°); similarly, the constellation Ursa Major can be
located by its position on the celestial sphere:
R.A.: 11hr; Dec: +50° .
The celestial analog to Earth latitude is called Declination, or
"Dec", and is measured in degrees, minutes and seconds (e.g.,
15° 27' 33"). Declination shown as north of the celestial equator
is indicated with a "+" sign in front of the measurement (e.g., the
Declination of the North Celestial Pole is +90°), with Declination
shown as south of the celestial equator indicated with a "–" sign