Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Example: Aggregate Marking with Oversubscription Rate-Limiting Hierarchical Policy
105
Appendix B
Applying a ToS Mark to Color-Coded
Packets in Aggregate Rate-Limit
Hierarchical Policies
The information provided in this appendix updates the
Example: Aggregate Marking
with Oversubscription Rate-Limiting Hierarchical Policy section
in
Chapter 5, Creating
Rate-Limit Profiles of the JunosE Policy Management Configuration Guide
.
Example: Aggregate Marking with Oversubscription Rate-Limiting Hierarchical Policy
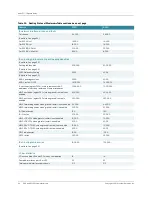
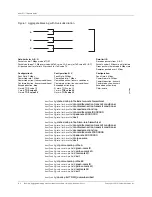
Figure 1 shows an aggregate rate limit that enables up to 2 Mbps of traffic to be sent
with a ToS value marked as 10. Traffic above that rate is sent with a ToS value marked
as 20 or 30 (depending on packet type) and traffic above 6 Mbps is dropped. The 2
Mbps of traffic with the ToS value of 10 is oversubscribed among individual flows A, B,
and C, each of which can have up to 1 Mbps of traffic with the ToS value of 10. An
individual flow can mark a packet with the ToS value of 10, but if there is insufficient
bandwidth at the shared rate limit because of oversubscription, the packet is demoted
and remarked.
The demoted packets from flow A are marked with the ToS value of 20 but the
demoted packets from flows B and C are marked with the ToS value of 30. The shared
rate limit determines whether to demote the packet, in which case each individual rate
limit selects the new ToS marking. Individual flows are not required to mark demoted
packets with the same value.
The committed and conformed actions are transmit conditional so that all packets
also go through rate limit S, because rate limit S imposes the limit of 2 Mbps of traffic
with the ToS value of 10 (total across A, B, and C).
Committed packets are transmitted conditionally to rate limit S, which has a peak rate
of 6 Mbps and a committed rate of 2 Mbps; these packets can be demoted by S to Y
(yellow), in which case they are remarked with the ToS value of 20 or 30. If S leaves
them as G (green), they are marked with the ToS value of 10. All conformed packets
from A, B, and C are also transmitted conditionally to S but arrive as Y because rate
limits do not promote packets in color. S is color-aware so these Y packets do not take
away G tokens, leaving them reserved only for the G packets coming from A, B, and C.