30
IBM eX5 Implementation Guide
RBS operates automatically without issuing a Predictive Failure Analysis (PFA) or light path
diagnostics alert to the administrator, although an event is logged to the service processor
log. After the second DIMM failure, PFA and light path diagnostics alerts occur on that DIMM
normally.
Lock step
IBM eX5 memory operates in lock step mode. Lock step is a memory protection feature that
involves the pairing of two memory DIMMs. The paired DIMMs can perform the same
operations and the results are compared. If any discrepancies exist between the results, a
memory error is signaled. Lock step mode gives a maximum of 64 GB of usable memory with
one CPU installed, and 128 GB of usable memory with two CPUs installed (using 8 GB
DIMMs).
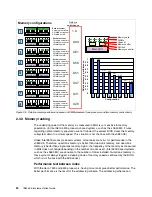
Memory must be installed in pairs of two identical DIMMs per processor. Although the size of
the DIMM pairs installed can differ, the pairs must be of the same speed.
Machine Check Architecture (MCA)
MCA is a RAS feature that has previously only been available for other processor
architectures, such as Intel Itanium®, IBM POWER®, and other reduced instruction set
computing (RISC) processors, and mainframes. Implementation of the MCA requires
hardware support, firmware support, such as the UEFI, and operating system support.
The MCA enables system-error handling that otherwise requires stopping the operating
system. For example, if a memory location in a DIMM no longer functions properly and it
cannot be recovered by the DIMM or memory controller logic, MCA logs the failure and
prevents that memory location from being used. If the memory location was in use by a thread
at the time, the process that owns the thread is terminated.
Microsoft, Novell, Red Hat, VMware, and other operating system vendors have announced
support for the Intel MCA on the Xeon processors.
Scalable memory buffers
Unlike the Xeon 5500 and 5600 series, which use unbuffered memory channels, the Xeon
6500 and 7500 processors use scalable memory buffers in the systems design. This
approach reflects the various workloads for which these processors were intended. The 6500
and 7500 family processors are designed for workloads requiring more memory, such as
virtualization and databases. The use of scalable memory buffers allows more memory per
processor, and prevents memory bandwidth reductions when more memory is added per
processor.
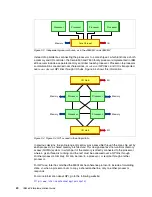
2.3.7 I/O hubs
The connection to I/O devices (such as keyboard, mouse, and USB) and to I/O adapters
(such as hard disk drive controllers, Ethernet network interfaces, and Fibre Channel host bus
adapters) is handled by I/O hubs, which then connect to the processors through QPI links.
Figure 2-4 on page 20 shows the I/O hub connectivity. Connections to the I/O devices are
fault tolerant, because data can be routed over either of the two QPI links to each I/O hub. For
optimal system performance in the four processor systems (with two I/O hubs), balance the
high-throughput adapters across the I/O hubs.
Содержание x3850 X5
Страница 2: ......
Страница 3: ...International Technical Support Organization IBM eX5 Implementation Guide May 2011 SG24 7909 00...
Страница 20: ...xviii IBM eX5 Implementation Guide...
Страница 32: ...12 IBM eX5 Implementation Guide...
Страница 34: ...14 IBM eX5 Implementation Guide...
Страница 74: ...54 IBM eX5 Implementation Guide...
Страница 136: ...116 IBM eX5 Implementation Guide...
Страница 238: ...218 IBM eX5 Implementation Guide...
Страница 392: ...372 IBM eX5 Implementation Guide...
Страница 466: ...446 IBM eX5 Implementation Guide...
Страница 484: ...464 IBM eX5 Implementation Guide Figure 9 14 IMM Remote Control Video Viewer showing power control options...
Страница 560: ...540 IBM eX5 Implementation Guide...
Страница 564: ...544 IBM eX5 Implementation Guide...
Страница 578: ...IBM eX5 Implementation Guide IBM eX5 Implementation Guide...
Страница 579: ......