LTE CPE B2368 User's
Guide
8 Network Address Translation (NAT)
Issue 01
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
66
8
Network Address Translation (NAT)
8
Network Address Translation (NAT)
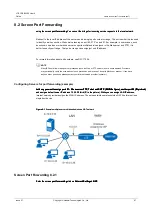
8.1 Overview
NAT (Network Address Translation - NAT, see the definition of RFC 1631) is in computer networks method
of modifying traffic passing through the router rewriting the source or destination IP addresses, or even
heads higher layer protocols.
8.1.1 What You Need to Know
Before reading this chapter is to be familiar with the following terms.
Internal / external and global / local
Parameter internal / external host indicates the position relative to the LTE modem. For example, computers and
devices in your home network, the internal host devices, while the web servers on the Internet are external host
device.
Parameter global / local refers to the IP address of the host device in the packet as it passes through the router. The
local address refers to the IP address of the host device when moving a packet on the local network, while global
address is the IP address of the host device in the packet data stream identical WAN.
NAT
Basically, NAT changes the source IP address of a data packet from the customer (ie internal, local address) to
another (the inside global) before directing the packet to the WAN. Once a response is received, performs NAT
destination address (the inside global) back to the inside local address, before directing the visitors to the internal
device.
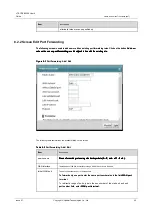
port forwarding
Port forwarding is a list of internal (ie. Hidden behind NAT on the LAN) servers, such as Web or FTP, which can be
made visible from the outside, even though it operates through NAT entire internal network from the outside as a
single computer.
More information
A more detailed description of the NAT technology is contained in chapter 8.6 Technical details.