46
[SwitchS] display ip routing-table 4.4.4.4 verbose
Routing Table : Public
Summary Count : 1
Destination: 4.4.4.4/32
Protocol: RIP Process ID: 1
Preference: 100 Cost: 1
IpPrecedence: QosLcId:
NextHop: 13.13.13.2 Interface: vlan200
BkNextHop: 12.12.12.2 BkInterface: vlan100
RelyNextHop: 0.0.0.0 Neighbor : 0.0.0.0
Tunnel ID: 0x0 Label: NULL
BKTunnel ID: 0x0 BKLabel: NULL
State: Active Adv Age: 00h01m27s
Tag: 0
# Display route 1.1.1.1/32 on Switch D to view the backup next hop information.
[SwitchD] display ip routing-table 1.1.1.1 verbose
Routing Table : Public
Summary Count : 1
Destination: 1.1.1.1/32
Protocol: RIP Process ID: 1
Preference: 100 Cost: 1
IpPrecedence: QosLcId:
NextHop: 13.13.13.1 Interface: vlan200
BkNextHop: 24.24.24.2 BkInterface: vlan101
RelyNextHop: 0.0.0.0 Neighbor : 0.0.0.0
Tunnel ID: 0x0 Label: NULL
BKTunnel ID: 0x0 BKLabel: NULL
State: Active Adv Age: 00h01m27s
Tag: 0
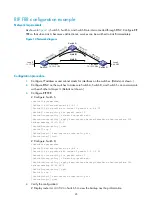
Configuring BFD for RIP (single-hop echo detection mode)
Network requirements
In the following figure, Switch A and Switch C are interconnected through a Layer 2 switch.
VLAN-interface 100 of the two switches runs RIP process 1, BFD is enabled on VLAN-interface 100 of
Switch A.
Switch A is connected to Switch C through Switch B. VLAN-interface 200 on Switch A runs RIP process
2; VLAN-interface 300 on Switch C, and VLAN-interface 200 and VLAN-interface 300 on Switch B run
RIP process 1.
Configure a static route and enable static route redistribution into RIP on Switch C. Switch A learns the
static route sent by Switch C, the output interface of the route is the interface connected to the Layer 2
switch.
Configure BFD so that when the link between Switch C and the Layer 2 switch fails, BFD can quickly
detect the link failure and notify it to RIP, and the BFD session goes down. In response, RIP deletes the
neighbor relationship with Switch C and the route information received from Switch C. Then, Switch A