116
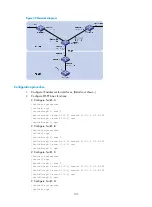
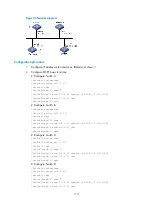
Figure 45
Network diagram
Configuration procedure
1.
Configure IP addresses for interfaces. (Details not shown.)
2.
Configure OSPF basic functions:
# Configure Switch A
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] router id 1.1.1.1
[SwitchA] ospf 100
[SwitchA-ospf-100] area 0
[SwitchA-ospf-100-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[SwitchA-ospf-100-area-0.0.0.0] quit
# Configure Switch B
<SwitchB> system-view
[SwitchB] router id 2.2.2.2
[SwitchB] ospf 100
[SwitchB-ospf-100] area 0
[SwitchB-ospf-100-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[SwitchB-ospf-100-area-0.0.0.0] quit
# Configure Switch C
<SwitchC> system-view
[SwitchC] router id 3.3.3.3
[SwitchC] ospf 100
[SwitchC-ospf-100] area 0
[SwitchC-ospf-100-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[SwitchC-ospf-100-area-0.0.0.0] quit
3.
Configure OSPF GR:
# Configure Switch A as the non-IETF standard OSPF GR Restarter: enable the link-local signaling
capability, the out-of-band re-synchronization capability, and non IETF standard Graceful Restart
capability for OSPF process 100.
[SwitchA-ospf-100] enable link-local-signaling
[SwitchA-ospf-100] enable out-of-band-resynchronization
[SwitchA-ospf-100] graceful-restart
[SwitchA-ospf-100] return
# Configure Switch B as the GR Helper: enable the link-local signaling capability and the
out-of-band re-synchronization capability for OSPF process 100.