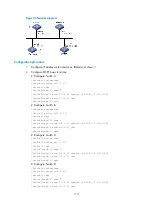
107
[SwitchC-ospf-1] quit
# Display OSPF routing information on Switch C
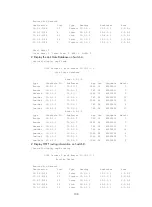
[SwitchC] display ospf routing
OSPF Process 1 with Router ID 10.4.1.1
Routing Tables
Routing for Network
Destination Cost Type NextHop AdvRouter Area
0.0.0.0/0 4 Inter 10.2.1.1 10.2.1.1 0.0.0.1
10.2.1.0/24 3 Transit 10.2.1.2 10.2.1.1 0.0.0.1
10.3.1.0/24 7 Inter 10.2.1.1 10.2.1.1 0.0.0.1
10.4.1.0/24 3 Stub 10.4.1.1 10.4.1.1 0.0.0.1
10.5.1.0/24 17 Inter 10.2.1.1 10.2.1.1 0.0.0.1
10.1.1.0/24 5 Inter 10.2.1.1 10.2.1.1 0.0.0.1
Total Nets: 6
Intra Area: 2 Inter Area: 4 ASE: 0 NSSA: 0
The output shows that when Switch C resides in the stub area, a default route takes the place of the
external route.
# Filter Type-3 LSAs out the stub area
[SwitchA] ospf
[SwitchA-ospf-1] area 1
[SwitchA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] stub no-summary
[SwitchA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] quit
# Display OSPF routing information on Switch C.
[SwitchC] display ospf routing
OSPF Process 1 with Router ID 10.4.1.1
Routing Tables
Routing for Network
Destination Cost Type NextHop AdvRouter Area
0.0.0.0/0 4 Inter 10.2.1.1 10.2.1.1 0.0.0.1
10.2.1.0/24 3 Transit 10.2.1.2 10.4.1.1 0.0.0.1
10.4.1.0/24 3 Stub 10.4.1.1 10.4.1.1 0.0.0.1
Total Nets: 3
Intra Area: 2 Inter Area: 1 ASE: 0 NSSA: 0
After this configuration, routing entries on the stub router are further reduced, containing only one
default external route.
Configuring an OSPF NSSA area
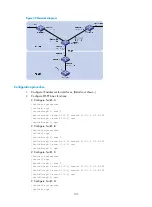
Network requirements
shows an AS is split into three areas, where all switches run OSPF. Switch A and Switch B act
as ABRs to forward routing information between areas.