479
check is successful, the system reboots the device. Otherwise, a dialog box appears, telling you
that the current configuration and the saved configuration are inconsistent, and the reboot fails.
In this case, save the current configuration manually before you can reboot the device.
If you do not select the option, the system reboots the device directly.
2.
Click
Apply
.
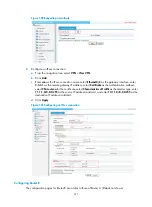
Figure 508
Rebooting the device
Managing services
This module provides six types of services: FTP, Telnet, SSH, SFTP, HTTP, and HTTPS. You can enable or
disable these services to enhance system performance and security and implement secure device
management.
This module also provides the function to modify HTTP and HTTPS port numbers, and the function to
associate the FTP, HTTP, or HTTPS service with an ACL, reducing attacks of illegal users on these services.
The description of the services is as follows:
•
FTP service
—Transfers files between server and client over a TCP/IP network.
•
Telnet service
—Provides remote login and virtual terminal functions on the network.
•
SSH
service
—Offers a method for securely logging in to a remote device. By encryption and strong
authentication, SSH protects devices against attacks such as IP spoofing and plain text password
interception.
•
SFTP service
—Uses the SSH connection to provide secure data transfer. The device can serve as the
SFTP server, allowing a remote user to log in to the SFTP server for secure file management and
transfer. The device can also serve as an SFTP client, enabling a user to log in from the device to a
remote device for secure file transfer. It is a new feature in SSH2.0.
•
HTTP service
—Transfers Web page information across the Internet. It is an application-layer
protocol in the TCP/IP protocol suite. You can log in to the device by using the HTTP protocol with
HTTP service enabled, accessing and controlling the device with Web-based network
management.
•
HTTPS service
—Secures data transmission through SSL as follows:
Uses the SSL protocol to ensure the legal clients to access the device securely and prohibit the
illegal clients.
Encrypts the data exchanged between the HTTPS client and the device to ensure the data
security and integrity, realizing the security management of the device.
Defines certificate attribute-based access control policy for the device to control the access right
of the client to further avoid attacks from illegal clients.
Содержание MSR SERIES
Страница 17: ...xv Documents 835 Websites 835 Conventions 836 Index 838 ...
Страница 20: ...3 Figure 3 Initial page of the Web interface ...
Страница 42: ...25 Figure 13 Firefox Web browser setting ...
Страница 59: ...42 Figure 27 Checking the basic service configuration ...
Страница 73: ...56 Figure 35 Sample interface statistics ...
Страница 156: ...139 Figure 139 Rebooting the 3G modem ...
Страница 168: ...151 Figure 152 Configuring Web server 2 ...
Страница 174: ...157 Figure 158 Configure the URL filtering function ...
Страница 187: ...170 Upon detecting the Land or Smurf attack on Ethernet 0 2 Router outputs an alarm log and drops the attack packet ...
Страница 242: ...225 Figure 233 Enabling the DHCP client on interface Ethernet 0 1 ...
Страница 247: ...230 Figure 236 The page for configuring an advanced IPv4 ACL ...
Страница 255: ...238 Figure 241 Advanced limit setting ...
Страница 298: ...281 e Click Apply 2 Configure Router B in the same way Router A is configured ...
Страница 354: ...337 Figure 339 Configuring a login control rule so Host B cannot access Router through the Web ...
Страница 400: ...383 Figure 387 Verifying the configuration ...
Страница 405: ...388 ...
Страница 523: ...506 Figure 530 Ping configuration page ...
Страница 538: ...521 a Click Device A on the topology diagram b Click Ethernet 0 2 on the panel diagram c Click Port Guard ...
Страница 744: ...727 Verifying the configuration In the case that the IP network is unavailable calls can be made over PSTN ...
Страница 775: ...758 Figure 785 Configuring a jump node ...
Страница 791: ...774 Figure 801 Configuring a jump node ...