272
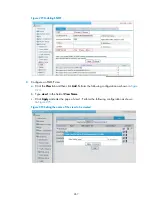
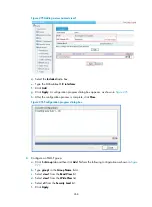
Configuring bridging
Through the Web interface, you can configure the following transparent bridging functions:
•
Enabling a bridge set
•
Adding an interface to a bridge set
Overview
A bridge is a store-and-forward device that connects and transfers traffic between LAN segments at the
data-link layer. In some small-sized networks, especially those with dispersed distribution of users, the use
of bridges can reduce the network maintenance costs without requiring the end users to perform special
configurations on the devices.
In applications, the following major kinds of bridging technologies apply: transparent bridging,
source-route bridging (SRB), translational bridging, and source-route translational bridging (SR/TLB).
The devices support only transparent bridging.
Transparent bridging bridges LAN segments of the same physical media type, primarily in Ethernet
environments. A transparent bridging device keeps a bridge table, which contains mappings between
destination MAC addresses and outbound interfaces.
For more information about transparent bridging, see
Layer 2—WAN Configuration Guide
in
HP MSR
Router Series Configuration Guides (V5)
.
Major functionalities of bridges
Maintaining the bridge table
A bridge relies on its bridge table to forward data. A bridge table consists two parts: MAC address list
and interface list. Once connected to a physical LAN segment, a bridge listens to all Ethernet frames on
the segments. When it receives an Ethernet frame, it extracts the source MAC address of the frame and
creates a mapping entry between this MAC address and the interface on which the Ethernet frame was
received.
As shown in
, Host A, Host B, Host C, and Host D are attached to two LAN segments. Host A
and Host B are connected to bridge interface 1. When Host A sends an Ethernet frame to Host B, both
bridging interface 1 and Host B receive this frame.
Содержание MSR SERIES
Страница 17: ...xv Documents 835 Websites 835 Conventions 836 Index 838 ...
Страница 20: ...3 Figure 3 Initial page of the Web interface ...
Страница 42: ...25 Figure 13 Firefox Web browser setting ...
Страница 59: ...42 Figure 27 Checking the basic service configuration ...
Страница 73: ...56 Figure 35 Sample interface statistics ...
Страница 156: ...139 Figure 139 Rebooting the 3G modem ...
Страница 168: ...151 Figure 152 Configuring Web server 2 ...
Страница 174: ...157 Figure 158 Configure the URL filtering function ...
Страница 187: ...170 Upon detecting the Land or Smurf attack on Ethernet 0 2 Router outputs an alarm log and drops the attack packet ...
Страница 242: ...225 Figure 233 Enabling the DHCP client on interface Ethernet 0 1 ...
Страница 247: ...230 Figure 236 The page for configuring an advanced IPv4 ACL ...
Страница 255: ...238 Figure 241 Advanced limit setting ...
Страница 298: ...281 e Click Apply 2 Configure Router B in the same way Router A is configured ...
Страница 354: ...337 Figure 339 Configuring a login control rule so Host B cannot access Router through the Web ...
Страница 400: ...383 Figure 387 Verifying the configuration ...
Страница 405: ...388 ...
Страница 523: ...506 Figure 530 Ping configuration page ...
Страница 538: ...521 a Click Device A on the topology diagram b Click Ethernet 0 2 on the panel diagram c Click Port Guard ...
Страница 744: ...727 Verifying the configuration In the case that the IP network is unavailable calls can be made over PSTN ...
Страница 775: ...758 Figure 785 Configuring a jump node ...
Страница 791: ...774 Figure 801 Configuring a jump node ...