52
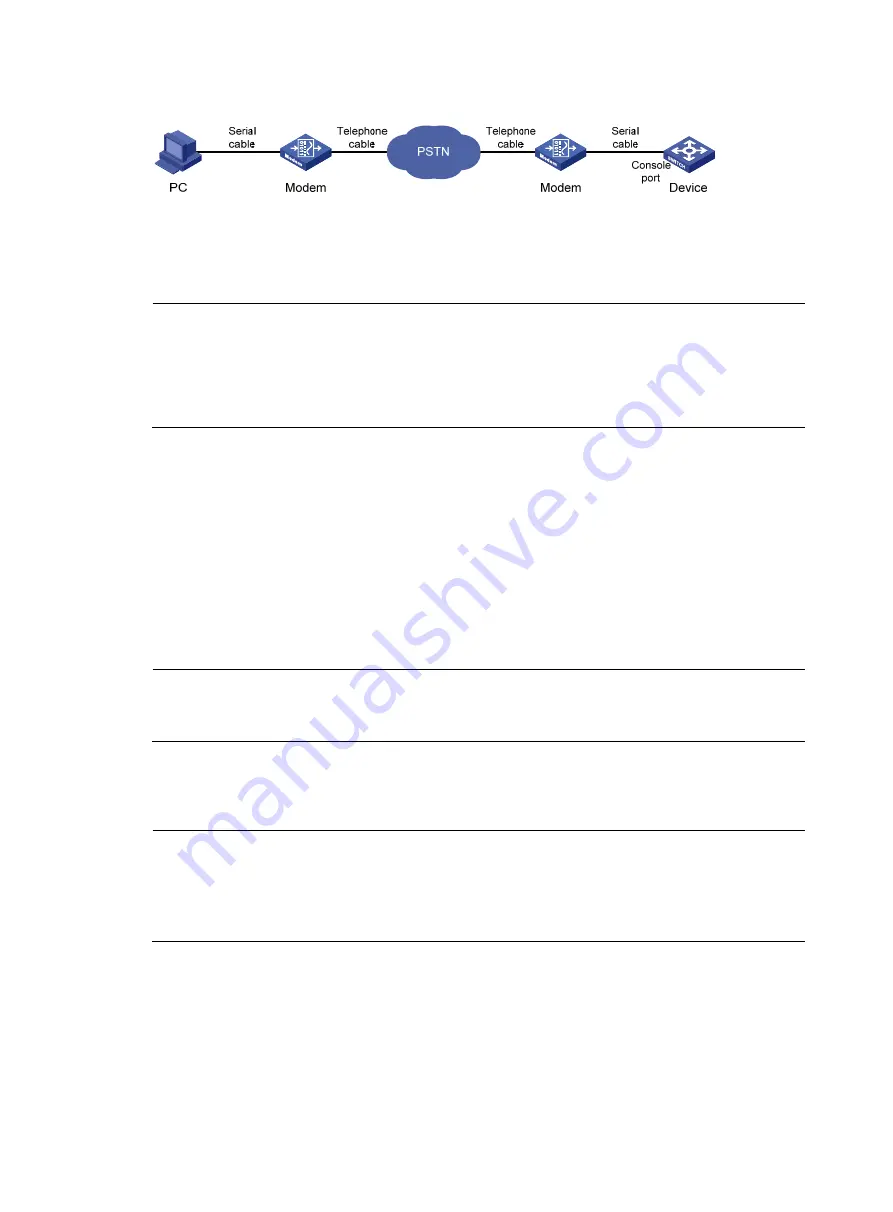
Figure 15
Set up a configuration terminal
2.
Configuration on the administrator side
The PC and the modem are correctly connected, the modem is connected to a telephone cable, and the
telephone number of the remote modem connected to the Console port of the remote switch is obtained.
NOTE:
On the device:
•
The baud rate of the Console port is lower than the transmission rate of the modem. Otherwise, packets
may be lost.
•
The parity check mode, stop bits, and data bits of the Console port adopt the default settings.
3.
Perform the following configurations on the modem that is directly connected to the device:
AT&F
----------------------- Restore the factory defaults
ATS0=1
----------------------- Configure auto-answer on first ring
AT&D
----------------------- Ignore data Terminal Ready signals
AT&K0
----------------------- Disable local flow control
AT&R1
----------------------- Ignore Data Flow Control signals
AT&S0 -----------------------
Force
DSR
to remain on
ATEQ1&W ----------------------- Disable the modem from response to commands and save the
configuration
To verify your configuration, enter AT&V to show the configuration results.
NOTE:
The configuration commands and the output for different modems may be different. For more information,
see the user guide of your modem.
4.
Launch a terminal emulation utility (such as HyperTerminal in Windows XP/Windows 2000),
create a new connection (the telephone number is the number of the modem connected to the
device).
NOTE:
On Windows 2003 Server operating system, you need to add the HyperTerminal program first, and then
log in to and manage the device as described in this document. On Windows 2008 Server, Windows 7,
Windows Vista, or some other operating system, you need to obtain a third party terminal control
program first, and follow the user guide or online help of that program to log in to the device.
5.
Dial the destination number on the PC to establish a connection with the device, as shown in
through
.
















































