198
PKI configuration examples
CAUTION:
When the CA uses Windows Server, the SCEP add-on is required, and you must use the
certificate request from
ra
command to specify that the entity request a certificate from an RA.
When the CA uses RSA Keon, the SCEP add-on is not required, and you must use the
certificate request from
ca
command to specify that the entity request a certificate from a CA.
Requesting a certificate from a CA running RSA Keon
NOTE:
The CA server runs RSA Keon in this configuration example.
Network requirements
The device submits a local certificate request to the CA server.
The device acquires the CRLs for certificate verification.
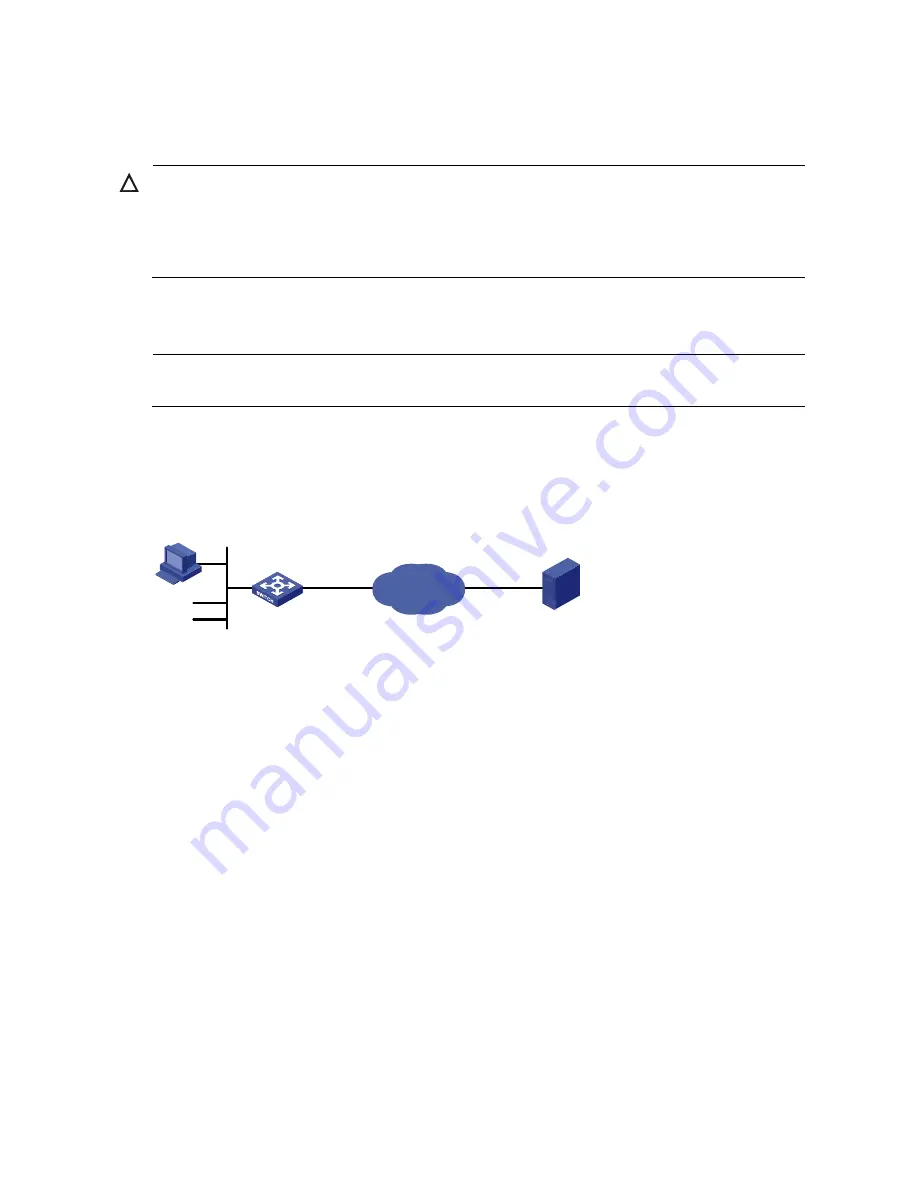
Figure 55
Request a certificate from a CA running RSA Keon
CA server
Internet
Host
Switch
PKI entity
Configuration procedure
1.
Configure the CA server
# Create a CA server named
myca
.
In this example, configure these basic attributes on the CA server at first:
Nickname—Name of the trusted CA.
Subject DN—DN information of the CA, including the Common Name (CN), Organization Unit
(OU), Organization (O), and Country (C).
The other attributes might be left using the default values.
# Configure extended attributes.
After configuring the basic attributes, perform configuration on the jurisdiction configuration page of the
CA server. This includes selecting the proper extension profiles, enabling the SCEP autovetting function,
and adding the IP address list for SCEP autovetting.
# Configure the CRL distribution behavior.
After completing the configuration, you must perform CRL related configurations. In this example, select
the local CRL distribution mode of HTTP and set the HTTP URL to http://4.4.4.133:447/myca.crl.
After the configuration, make sure that the system clock of the device is synchronous to that of the CA, so
that the device can request certificates and retrieve CRLs properly.
















































