235
The route between the CE and the PE can be a static route, RIP route, OSPF route, IS-IS route, EBGP route,
or IBGP route. No matter which routing protocol is used, the CE always advertises standard IPv4 routes
to the PE.
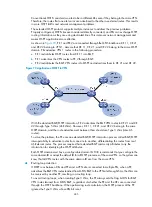
Routing information exchange from the ingress PE to the egress PE
After learning the VPN routing information from the CE, the ingress PE adds RDs and route targets for
these standard IPv4 routes to create VPN-IPv4 routes, save them to the routing table of the VPN instance
that is created for the CE, and then trigger MPLS to assign VPN labels for them.
Then, the ingress PE advertises the VPN-IPv4 routes to the egress PE through MP-BGP.
Finally, the egress PE compares the export target attribute of the VPN-IPv4 routes with the import target
attribute that it maintains for the VPN instance and determines whether to add the routes to the routing
table of the VPN instance.
PEs use IGP to ensure the connectivity between them.
Routing information exchange from the egress PE to the remote CE
A remote CE can learn VPN routes from the egress PE in a number of ways. The routes can be static routes,
RIP routes, OSPF routes, IS-IS routes, EBGP routes, and IBGP routes. The exchange of routing information
between the egress PE and the remote CE is the same as that between the local CE and the ingress PE.
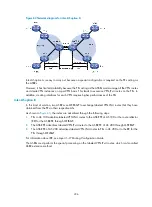
Inter-AS VPN
In some networking scenarios, multiple sites of a VPN are connected to multiple ISPs in different ASs, or
to multiple ASs of an ISP. Such an application is called inter-AS VPN.
RFC 2547bis presents the following inter-AS VPN solutions:
•
VRF-to-VRF
—ASBRs manage VPN routes between them through interfaces. This solution is also
called inter-AS option A.
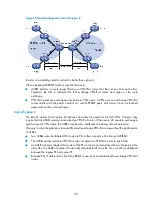
•
EBGP redistribution of labeled VPN-IPv4 routes
—ASBRs advertise labeled VPN-IPv4 routes to each
other through MP-EBGP. This solution is also called inter-AS option B.
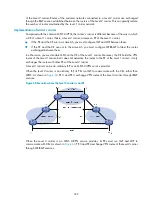
•
Multihop EBGP redistribution of labeled VPN-IPv4 routes
—PEs advertise labeled VPN-IPv4 routes
to each other through MP-EBGP. This solution is also called inter-AS option C.
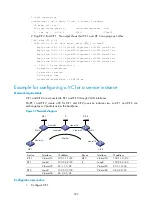
Inter-AS option A
In this solution, PEs of two ASs are directly connected and each PE is also the ASBR of its AS.
The PEs acting as ASBRs are connected through interfaces. Each of them treats the other as a CE of its
own and advertises IPv4 routes through conventional EBGP. Within an AS, packets are forwarded as
VPN packets by using two-level labels. Between ASBRs, conventional IP forwarding is used.
Ideally, each inter-AS VPN corresponds to a pair of interfaces, which exchange VPN routing information.