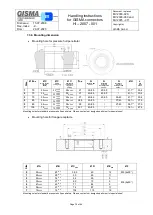
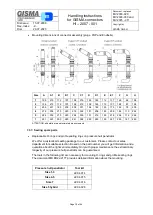
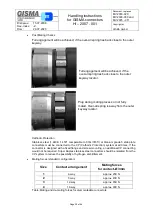
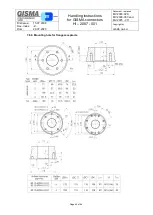
Handling instructions
for GISMA connectors
HI
– 2007 - 001
Document: replaces
MV 2000-020,
MV 2000-030 and
MV 2005 - 011
First issue:
15.07.2008
Rev.-Index: -Z-
From:
29.07.2020
Copyright by:
GISMA GmbH
Page 30 of 44
7.6.3.
Protection of receptacle’s pin contacts
Under no circumstances the contacts should be exposed to seawater with power off or on. If this
situation does occur the contact surfaces of the contacts will very rapidly degrade by electrolytic
action. If these damaged pins are subsequently mated into a socket insert there is a
very high
risk
of damage to the insulation and seals within the plug.
7.6.4. Removal of Marine Growth and Calcareous Deposits
To remove calcite growth topside or subsea from GISMA connectors, a solution of 50% Citric Acid
is recommended. All seawater exposed elastomeric materials in GISMA connectors have been
fully tested against 50% Citric Acid and are compatible for duration of 1 hour. In addition, the
thermoplastic materials have good resistance to Citric Acid.
Other acid cleaners, such as >50% Acetic Acid, should
not be
used as they may cause
deterioration of the elastomeric materials.
Chiselling and abrasive methods are not recommended. Use of a water jet is acceptable, but the
jet should not be directed onto the pins at the front and onto any elastomer part like insulators
and boot seals.
NOTE:
Keep the connector mated at any cleaning operation!