8 TROUBLESHOOTING
0463 766 001
-
70
-
© ESAB AB 2021
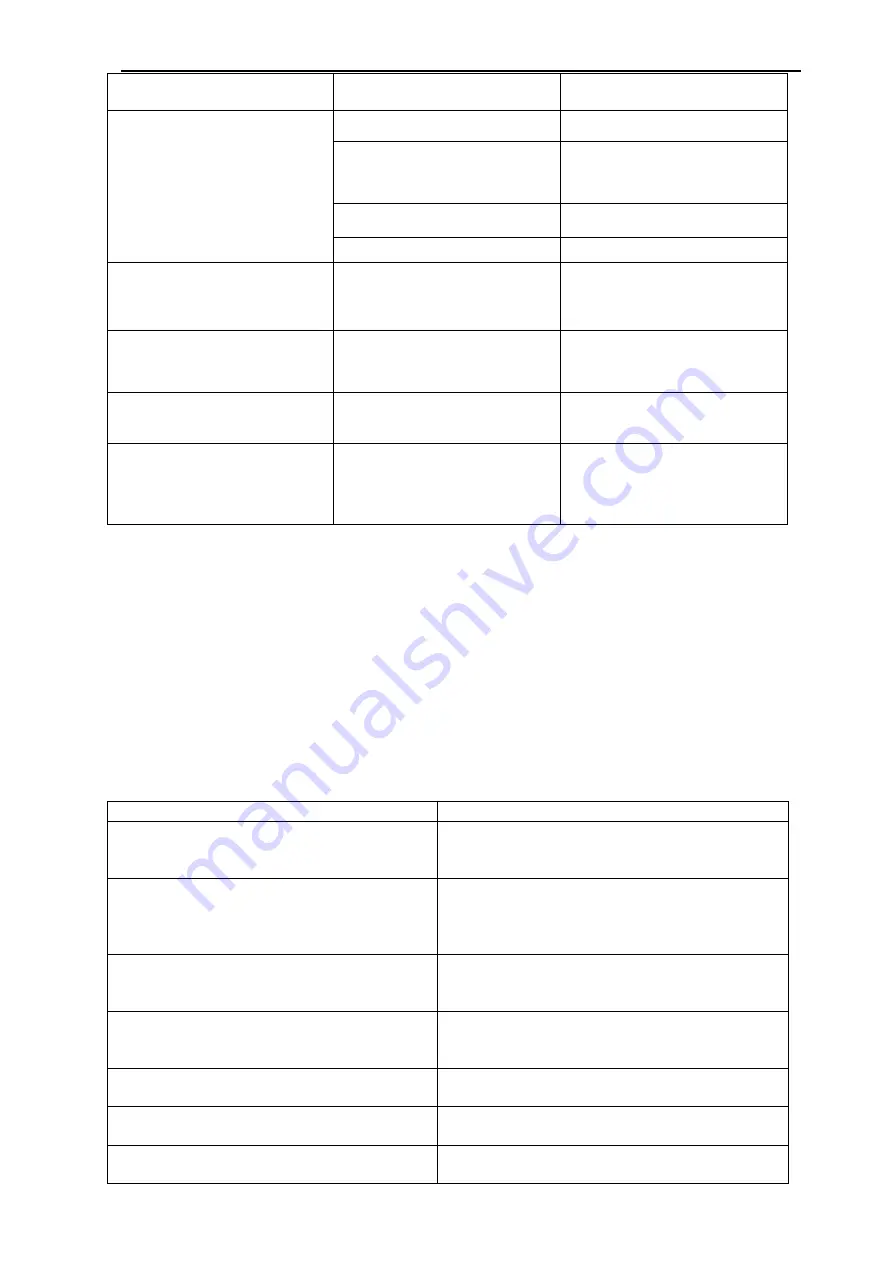
Type of fault
Cause
Corrective action
No gas flow in MIG mode.
The gas hose is damaged
Replace or repair.
Gas passage contains
impurities.
Disconnect the gas hose
from the rear of the power
source and blow out dirt.
Gas regulator turned OFF.
Turn ON regulator.
Empty gas cylinder.
Replace gas cylinder.
Gas flow continues after the
trigger switch has been
released (MIG mode).
Gas valve has jammed
open due to dirt in the gas
or the gas line.
Contact an authorised
ESAB service technician.
Power indicator will not
illuminate and welding arc
cannot be established.
The electricity supply has
exceeded voltage limits of
the power source.
Ensure that the electricity
supply is within 120 V ±10%
or 230 VAC ±10%.
TIG electrode melts when
arc is struck.
The TIG torch is connected
to the (+) VE terminal.
Connect the TIG torch to
the (-) VE terminal.
Arc flutters during TIG
welding.
Tungsten electrode is too
large for the welding
current.
Select the correct size of
tungsten electrode. See
"TIG (L-GTAW) basic
welding technique" section.
8.2
MIG
(GMAW/FCAW)
welding
troubleshooting
Solving
problems
beyond
the
welding
terminals
The general approach to fix MIG (GMAW/FCAW) welding problems is to start at the wire spool
then work through to the MIG gun. There are two main areas where problems occur with GMAW,
porosity and inconsistent wire feed.
Porosity
When there is a gas problem, the result is usually porosity within the weld metal. Porosity always
stems from some contaminant within the molten weld pool which is in the process of escaping
during solidification of the molten metal. Contaminants range from no gas around the welding arc
to dirt on the work piece surface. Porosity can be reduced by checking the following points.
Table
23:
Porosity
Type of fault
Corrective action
No shielding gas or wrong flow meter
settings.
Ensure that the shielding gas cylinder is not
empty and the flow meter is correctly
adjusted to 31.75 CFH.
No shielding gas or wrong flow gauge.
Ensure that the shielding gas cylinder is not
empty and the flow meter is correctly
adjusted to workshop welding: 28-35 CFH or
outdoors welding: 35-46 CFH.
Gas leaks.
Check for gas leaks between the
regulator/cylinder connection and in the gas
hose to the power source.
Internal gas hose in the power source.
Ensure the hose from the solenoid valve to
the MIG gun adapter has not fractured and
that it is connected to the MIG gun adapter.
Welding in a windy environment.
Shield the weld area from the wind or
increase the gas flow.
Dirty from welding, oily, painted, oxidized
or greasy plate.
Clean contaminates off the workpiece.
Distance between the MIG gun nozzle
and the workpiece.
Keep the distance between the MIG gun
nozzle and the workpiece to a minimum.













































