8
1.4.5 Power Supply Connection
This is the jack where you connect your external 48V DC power supply.
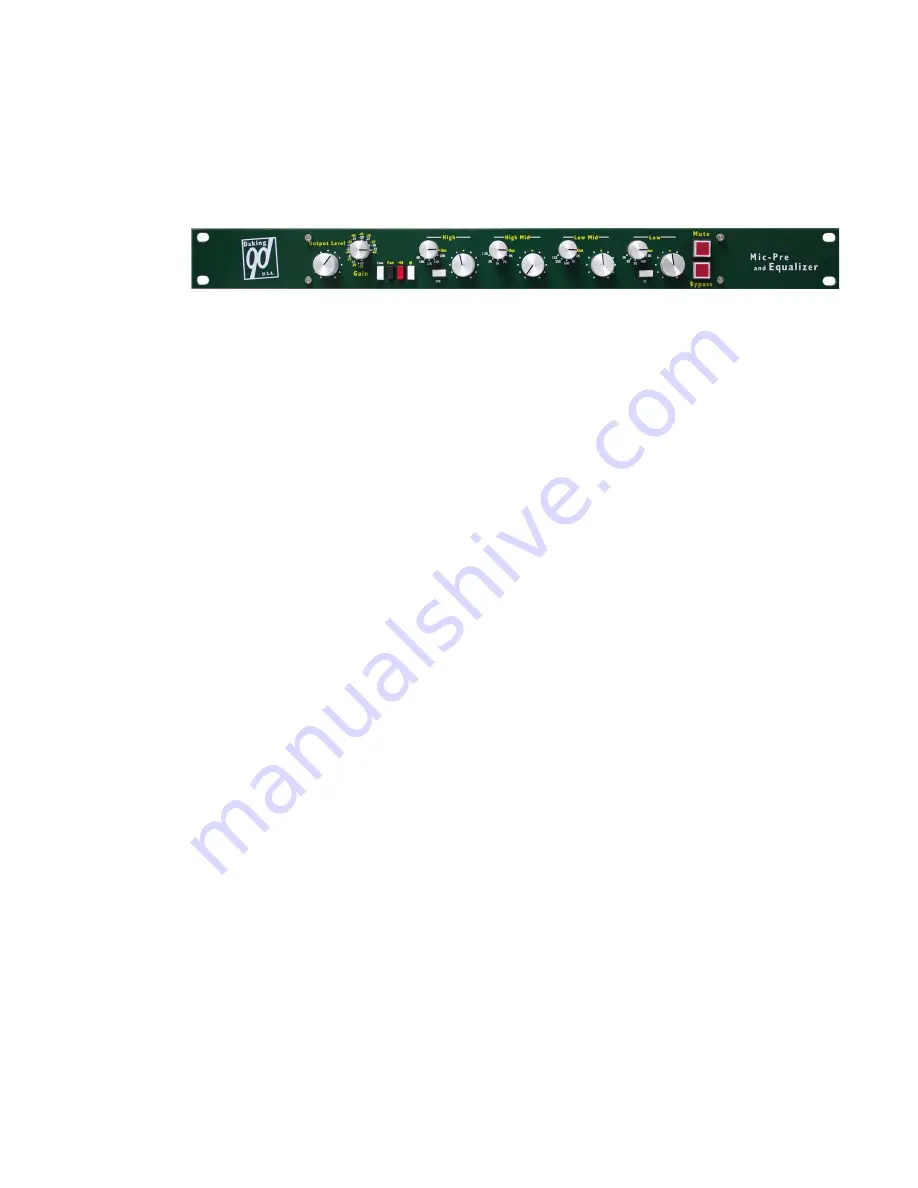
1.5 Front Panel: The Preamplifier Section
1.5.1 The Output Level Knob
The Output Level knob is akin to the fader on a channel on a mixer. You
use this to control the level leaving the Mic Pre EQ. If you are boosting
with the EQ heavily you will probably need to turn the output level down
and if you are cutting heavily with the EQ you may need to bring the level
up.
1.5.2 The Gain Knob
The Gain Knob allows you to control the amount of gain added to the
input signal. The knob is stepped in 5dB increments. The gain should be
set as high as possible without hearing audible clipping or distortion, or
overloading the following stage in the signal chain. For instance, your
Mic Pre EQ can support outputs up to +28dB, but most audio interfaces
clip at +18dB. The gain control would have to be set so as to not overload
the audio interface. Professional consoles are capable of handling levels
as high as +30dB in some cases.
1.5.3 The Line Button
The Line buttons switches the input of the Mic Pre EQ from the Mic Input
to the Line Input bypassing the microphone preamplifier.
1.5.4 Pad Button
The Pad button is a 20dB attenuator useful when the gain switch is in its
lowest position and the peak indicator (*) is still being lit. Most
commonly the Pad button will be required for extremely dynamic sources
like drums and percussion, or extremely loud sources like electric guitar
through a large amplifier. The Pad button only works on the microphone
input, not on the line input.
1.5.5 +48 Button
This button controls the 48 volt phantom power which is used to power
the onboard electronics in condenser microphones or active direct
injection (DI) boxes.












