Unintended Consequences
To explain this unintended traffic shaping, consider a client A that connects to host X with P2P
traffic and triggers an IDP rule with the
Pipe
action so the connection becomes subject to traffic
shaping. Now, if another client B also connects to host X but this time with web surfing traffic, an
IDP rule is not triggered but the connection should not be traffic shaped along with client A's
connection just because host X is involved.
Excluding Hosts
To avoid these unintended consequences, we specify the IPv4 addresses of client A and client B
in the
Network
range but not host X. This tells NetDefendOS that host X is not relevant in making
a decision about including new non-IDP-triggering connections in traffic shaping.
It may seem counter-intuitive that client B is also included in the
Network
range but this is done
on the assumption that client B is a user whose traffic might also have to be traffic shaped if they
become involved in a P2P transfer.
If
Network
is not specified then any connection involving either client A or host X will be subject
to traffic shaping and this is probably not desirable.
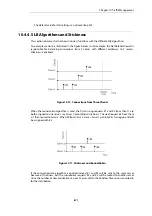
10.2.5. A P2P Scenario
The schematic below illustrates a typical scenario involving P2P data transfer. The sequence of
events is:
•
The client with IP address
192.168.1.15
initiates a P2P file transfer through a connection (1) to
the tracking server at
81.150.0.10
.
•
This connection triggers an IDP rule in NetDefendOS which is set up with an IDP signature
that targets the P2P application.
•
The
Pipe
action in the rule sets up a traffic shaping pipe with a specified capacity and the
connection is added to it.
•
A subsequent connection (2) to the file host at
92.92.92.92
occurs within the IDP rule's
Time
Window
and its traffic is therefore added to the pipe and is subject to shaping.
•
The client network to which
192.168.1.15
belongs, should ideally be included in the
Network
address range for the IDP rule.
Chapter 10: Traffic Management
800
Содержание NetDefendOS
Страница 30: ...Figure 1 3 Packet Flow Schematic Part III Chapter 1 NetDefendOS Overview 30 ...
Страница 32: ...Chapter 1 NetDefendOS Overview 32 ...
Страница 144: ...Chapter 2 Management and Maintenance 144 ...
Страница 220: ... Enable DHCP passthrough Enable L2 passthrough for non IP protocols 4 Click OK Chapter 3 Fundamentals 220 ...
Страница 267: ... SourceNetwork lannet DestinationInterface any DestinationNetwork all nets 4 Click OK Chapter 3 Fundamentals 267 ...
Страница 284: ...Chapter 3 Fundamentals 284 ...
Страница 360: ...The ospf command options are fully described in the separate NetDefendOS CLI Reference Guide Chapter 4 Routing 360 ...
Страница 392: ...Chapter 4 Routing 392 ...
Страница 396: ...Web Interface 1 Go to Network Ethernet If1 2 Select Enable DHCP 3 Click OK Chapter 5 DHCP Services 396 ...
Страница 419: ... Host 2001 DB8 1 MAC 00 90 12 13 14 15 5 Click OK Chapter 5 DHCP Services 419 ...
Страница 420: ...Chapter 5 DHCP Services 420 ...
Страница 424: ...2 Now enter Name lan_Access Action Expect Interface lan Network lannet 3 Click OK Chapter 6 Security Mechanisms 424 ...
Страница 573: ...Chapter 6 Security Mechanisms 573 ...
Страница 575: ...This section describes and provides examples of configuring NAT and SAT rules Chapter 7 Address Translation 575 ...
Страница 607: ...Chapter 7 Address Translation 607 ...
Страница 666: ...Chapter 8 User Authentication 666 ...
Страница 775: ...Chapter 9 VPN 775 ...
Страница 819: ...Chapter 10 Traffic Management 819 ...
Страница 842: ...Chapter 11 High Availability 842 ...
Страница 866: ...Default Enabled Chapter 13 Advanced Settings 866 ...
Страница 879: ...Chapter 13 Advanced Settings 879 ...