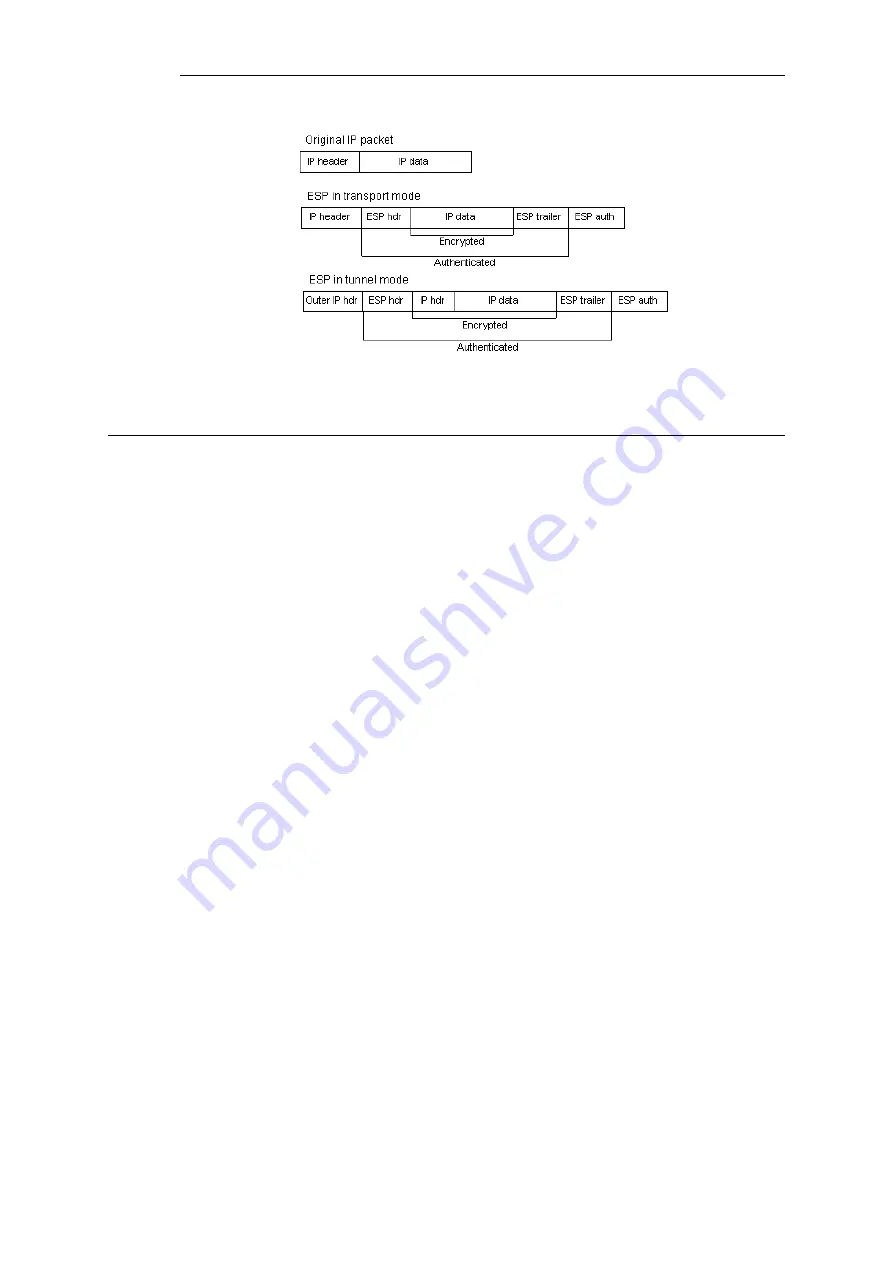
Figure 9.2. The ESP protocol
9.3.5. NAT Traversal
Both IKE and IPsec protocols present a problem in the functioning of NAT. Both protocols were
not designed to function with NAT and because of this, the technique called
NAT traversal
has
evolved. NAT traversal is an add-on to the IKE and IPsec protocols that allows them to function
when being NATed. NetDefendOS supports the RFC 3947 standard for NAT-Traversal with IKE.
NAT traversal is divided into two parts:
•
Additions to IKE that lets IPsec peers tell each other that they support NAT traversal, and the
specific versions supported. NetDefendOS supports the RFC 3947 standard for NAT-Traversal
with IKE.
•
Changes to the ESP encapsulation. If NAT traversal is used, ESP is encapsulated in UDP, which
allows for more flexible NATing.
Below, is a more detailed description of the changes made to the IKE and IPsec protocols.
NAT traversal is only used if both ends have support for it. For this purpose, NAT traversal aware
VPNs send out a special "vendor ID" to tell the other end of the tunnel that it understands NAT
traversal, and which specific versions of the draft it supports.
Achieving NAT Detection
To achieve NAT detection both IPsec peers send hashes of their own IP addresses along with the
source UDP port used in the IKE negotiations. This information is used to see whether the IP
address and source port each peer uses is the same as what the other peer sees. If the source
address and port have not changed, then the traffic has not been NATed along the way, and NAT
traversal is not necessary. If the source address and/or port has changed, then the traffic has
been NATed, and NAT traversal is used.
Changing Ports
Once the IPsec peers have decided that NAT traversal is necessary, the IKE negotiation is moved
away from UDP port 500 to port 4500. This is necessary since certain NAT devices treat UDP
packet on port 500 differently from other UDP packets in an effort to work around the NAT
problems with IKE. The problem is that this special handling of IKE packets may in fact break the
IKE negotiations, which is why the UDP port used by IKE has changed.
Chapter 9: VPN
693
Содержание NetDefendOS
Страница 30: ...Figure 1 3 Packet Flow Schematic Part III Chapter 1 NetDefendOS Overview 30 ...
Страница 32: ...Chapter 1 NetDefendOS Overview 32 ...
Страница 144: ...Chapter 2 Management and Maintenance 144 ...
Страница 220: ... Enable DHCP passthrough Enable L2 passthrough for non IP protocols 4 Click OK Chapter 3 Fundamentals 220 ...
Страница 267: ... SourceNetwork lannet DestinationInterface any DestinationNetwork all nets 4 Click OK Chapter 3 Fundamentals 267 ...
Страница 284: ...Chapter 3 Fundamentals 284 ...
Страница 360: ...The ospf command options are fully described in the separate NetDefendOS CLI Reference Guide Chapter 4 Routing 360 ...
Страница 392: ...Chapter 4 Routing 392 ...
Страница 396: ...Web Interface 1 Go to Network Ethernet If1 2 Select Enable DHCP 3 Click OK Chapter 5 DHCP Services 396 ...
Страница 419: ... Host 2001 DB8 1 MAC 00 90 12 13 14 15 5 Click OK Chapter 5 DHCP Services 419 ...
Страница 420: ...Chapter 5 DHCP Services 420 ...
Страница 424: ...2 Now enter Name lan_Access Action Expect Interface lan Network lannet 3 Click OK Chapter 6 Security Mechanisms 424 ...
Страница 573: ...Chapter 6 Security Mechanisms 573 ...
Страница 575: ...This section describes and provides examples of configuring NAT and SAT rules Chapter 7 Address Translation 575 ...
Страница 607: ...Chapter 7 Address Translation 607 ...
Страница 666: ...Chapter 8 User Authentication 666 ...
Страница 775: ...Chapter 9 VPN 775 ...
Страница 819: ...Chapter 10 Traffic Management 819 ...
Страница 842: ...Chapter 11 High Availability 842 ...
Страница 866: ...Default Enabled Chapter 13 Advanced Settings 866 ...
Страница 879: ...Chapter 13 Advanced Settings 879 ...









































