Design Considerations
AN64846 - Getting Started with CapSense
®
Doc. No. 001-64846 Rev. *X
85
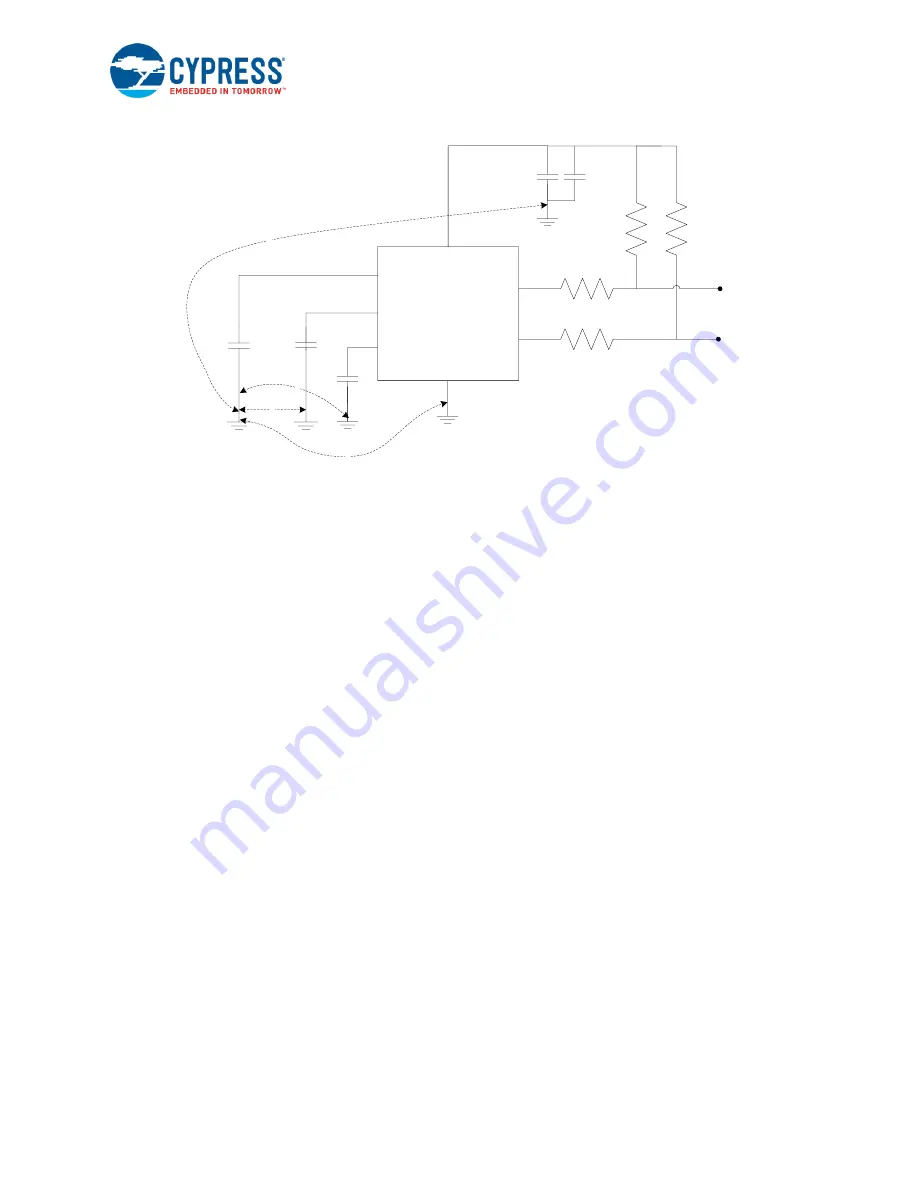
Figure 3-73. Important GND Nodes in CapSense Design
CY8CMBR3xxx
VCC
VDD
VSS
SCL
SDA
I2C
Connector
R1
R2
R3
R4
C1
C4
CMOD
C3
C2
CSx
C
p
(Sensor)
2
4
1
3
Sensor
GND
3.8.14 Shield Electrode and Guard Sensor
A shield electrode is a hatched fill that is driven with a signal which is the replica of the sensor signal. A shield electrode
is used for the following purposes:
Reduce sensor parasitic capacitance (C
P
):
In most of the CapSense applications it is recommended to have a
hatch fill in the top and bottom layer of the PCB surrounding the sensor and its traces. This hatch fill is connected
to ground for improved noise immunity. When a sensor has a large trace length it results in high sensor C
P
. High
sensor C
P
results is low sensor sensitivity and increases power consumption. To reduce the sensor C
P
you should
drive the hatch fill in the top and bottom layer with a driven shield signal.
Reduce the effect of nearby floating/grounded conductive objects:
section, shield electrode can be used to reduce the effect of floating/grounded
conductive
objects on proximity distance. In this case, the shield electrode should be placed in between the conductive object
and the proximity sensor, as shown in
Provide directionality to proximity sensing:
The electric field of a proximity sensor is omnidirectional and can
detect proximity in all directions. In most of the applications, it is required to detect proximity from only one direction.
In such cases, you can use a shield electrode to make the proximity sensor sense the target object in a single
direction.
Provide liquid tolerance:
section, shield electrodes prevent false triggers
due to the presence of liquid droplets on the CapSense sensor.
3.8.14.1 Shield Electrode for Proximity Sensing
If you want to use shield electrode for reducing sensor C
P
or reduce the effect of nearby floating/grounded conductive
objects or provide directionality to proximity sensing, follow the below guidelines:
To reduce the sensor C
P
, use a hatch fill of 0.17 mm (7 mil) trace and 1.143 mm (45 mil grid) in the top layer and
a hatch fill of 0.17 mm (7 mil) trace and 1.778 mm (70 mil grid) in the bottom layer and drive it with driven shield
signal.
To reduce the effect of floating/grounded conductive object on the proximity-sensing distance, place a hatch fill of
0.17 mm (7 mil) trace and 1.143 mm (45 mil grid) in between the sensor and the conductive object and drive the
hatch fill with the driven shield signal.
To make the proximity sensing unidirectional, place a hatch fill of 0.17 mm (7 mil) trace and 1.143 mm (45 mil grid)
in between the sensor and the direction in which proximity detection should be avoided and drive the hatch fill with
the driven shield signal.
















































