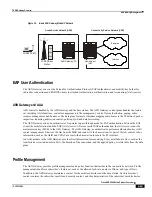
ASN Gateway Overview
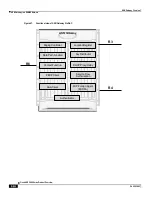
Supported Features ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview ▄
OL-22938-02
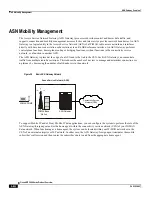
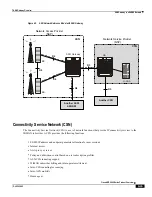
WiMAX R4 Inter-ASN Mobility Management
R4 inter-ASN mobility management procedures enable low latency call handovers between neighboring ASN Gateways
located in different geographical regions or different operator networks. During mobility operations, the call is anchored
on the anchor authenticator ASN Gateway. When a mobile subscriber roams to a destination cell site, the target base
station connects to the anchor gateway over the serving ASN Gateway‘s R4 interface. The R4 interface provides control
functions such as security context transfers and IP/GRE bearer level connections. The data conveyed to the subscriber
by the remote hosts is subsequently tunneled over R4 by the anchor authenticator gateway to the serving gateway. The
current ASN Gateway implementation supports the co-existence of anchor authenticator and anchor datapath functions
in the same ASN Gateway.
Supported R4 functionality includes:
R4 over Simple IP connections
R4 over Mobile IP connections
Anchor Gateway bi-casting over simultaneous R6 and R4 sessions
Co-location of DHCPv4 Proxy and PMIPv4 FA on anchor authenticator gateway
Support for multiple QoS service flows per-session via R4 tunnels
Important:
Both the anchor gateway session and non-anchor gateway sessions are counted towards the session
license separately. Licensed session limits are enforced based on the total number of anchor and non-anchor sessions.
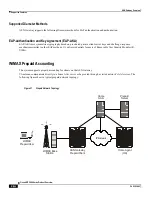
WiMAX R3 CSN Anchored Mobility Management
The R3 reference point defines a set of control plane protocols between the Access Service Network (ASN) and
Connectivity Service Network (CSN) to support AAA, policy enforcement, and mobility management functions. The
R3 reference interface is used in a mobile IP application with the home agent acting as the call anchor point. In contrast
to L2-based ASN anchored mobility procedures, CSN anchored mobility is L3-based and supports both proxy mobile IP
and mobile IP calls. The R3 interface uses mobile IP signaling and IP-in-IP tunneling or GRE tunneling and includes
standard features such as dynamic Home of Address (HoA) address allocation. Mobility signaling messages are
authenticated by the home agent based on a dynamic user identity called a pseudo-NAI which changes after each
authentication.
Mobile IP applications are well suited for inter-provider roaming applications and inter-technology handovers such as
WiMAX-HRPD Rev A, WiMAX-WiFi, and WiMAX-W-CDMA. Mobile IP also provides an attractive solution for
operators with a heterogeneous radio access network who want to support seamless mobility across base transfer
stations from multiple RAN suppliers.
Important:
Support for this function requires the HA feature license key.
Содержание ASR 5000 Series
Страница 1: ......
Страница 26: ......
Страница 48: ...New In Release 10 0 SCM Features Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview OL 22938 02 ...
Страница 50: ......
Страница 58: ......
Страница 67: ...Product Service and Feature Licenses Default Licenses Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview OL 22938 02 ...
Страница 68: ......
Страница 126: ......
Страница 138: ......
Страница 146: ......
Страница 218: ......
Страница 236: ......
Страница 356: ......
Страница 374: ......
Страница 422: ......
Страница 496: ......
Страница 572: ......
Страница 654: ......
Страница 700: ......
Страница 726: ......
Страница 784: ......
Страница 816: ......
Страница 839: ...Network Address Translation Overview How NAT Works Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview OL 22938 02 ...
Страница 841: ...Network Address Translation Overview How NAT Works Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview OL 22938 02 ...
Страница 844: ......
Страница 906: ......
Страница 926: ......
Страница 942: ......
Страница 943: ...Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview OL 22938 02 Chapter 30 Technical Specifications ...
Страница 966: ......
Страница 967: ...Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview OL 22938 02 Chapter 31 Safety Electrical and Environmental Certifications ...
Страница 972: ......