8-2
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Chapter 8 Controlling Mesh Access Points
Cisco Aironet Mesh Access Points
Cisco Aironet Mesh Access Points
Controller software release 5.2 supports these Cisco Aironet mesh access points:
•
Cisco Aironet 1520 series outdoor mesh access points
–
Cisco 1520 Series consists of the 1522 dual-radio mesh access point and the 1524 multi-radio
mesh access point.
Note
Refer to the
Cisco Aironet 1520 Series Outdoor Mesh Access Point Hardware Installation
Guide
for details on the physical installation and initial configuration of the mesh access
points at the following link:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps8368/tsd_products_support_series_home.html
•
Cisco Aironet 1130AG and 1240AG series indoor mesh access points
Note
AP1130 and AP1240 must be converted to operate as indoor mesh access points. Refer to
the
“Converting Indoor Access Points to Mesh Access Points (1130AG, 1240AG)” section
Note
All features discussed in this chapter apply to indoor (1130, 1240) and outdoor mesh access points
(1522, 1524) unless noted otherwise.
Mesh access point
or
MAP
is hereafter used to address both indoor
and outdoor mesh access points.
Note
Cisco Aironet 1505 and 1510 access points are not supported in this release.
Note
Refer to the
Release Notes for Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers and Mesh Access Points for Release 5.2.x
for mesh feature summary, operating notes and software upgrade steps for migrating from 4.1.19x.xx
mesh releases to controller release 5.2 at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6366/prod_release_notes_list.html.
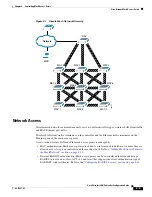
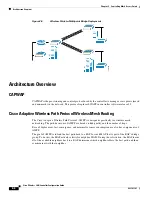
Access Point Roles
Access points within a mesh network operate as either a
root access point (RAP)
or a
mesh access point
(MAP)
.
RAPs have wired connections to their controller, and MAPs have wireless connections to their controller.
MAPs communicate among themselves and back to the RAP using wireless connections over the
802.11a radio backhaul. MAPs use the Cisco Adaptive Wireless Path Protocol (AWPP) to determine the
best path through the other mesh access points to the controller.
All the possible paths between the MAPs and RAPs form the wireless mesh network.
shows
the relationship between RAPs and MAPs in a mesh network.