1-15
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Chapter 1 Overview
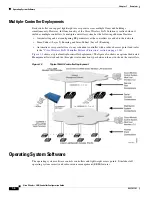
Startup Wizard
Startup Wizard
When a controller is powered up with a new factory operating system software load or after being reset
to factory defaults, the bootup script runs the Startup Wizard, which prompts the installer for initial
configuration. The Startup Wizard:
•
Ensures that the controller has a System Name, up to 32 characters.
•
Adds an Administrative username and password, each up to 24 characters.
•
Ensures that the controller can communicate with the GUI, CLI, or Cisco WCS (either directly or
indirectly) through the service port by accepting a valid IP configuration protocol (none or DHCP),
and if none, IP Address and netmask. If you do not want to use the service port, enter 0.0.0.0 for the
IP Address and netmask.
•
Ensures that the controller can communicate with the network (802.11 Distribution System) through
the management interface by collecting a valid static IP Address, netmask, default router IP address,
VLAN identifier, and physical port assignment.
•
Prompts for the IP address of the DHCP server used to supply IP addresses to clients, the controller
management interface, and optionally to the service port interface.
•
Collects the Virtual Gateway IP Address; any fictitious, unassigned IP address (such as 1.1.1.1) to
be used by Layer 3 Security and Mobility managers.
•
Allows you to enter the Mobility Group (RF Group) Name.
•
Collects the wireless LAN 1 802.11 SSID, or Network Name.
•
Asks you to define whether or not clients can use static IP addresses. Yes = more convenient, but
lower security (session can be hijacked), clients can supply their own IP Address, better for devices
that cannot use DHCP. No = less convenient, higher security, clients must DHCP for an IP Address,
works well for s XP devices.
•
If you want to configure a RADIUS server from the Startup Wizard, the RADIUS server IP address,
communication port, and Secret.
•
Collects the Country Code.
•
Enables or disables the 802.11a/n and 802.11b/g/n lightweight access point networks.
•
Enables or disables radio resource management (RRM).
To use the Startup Wizard, refer to the
“Using the Configuration Wizard” section on page 4-2
.
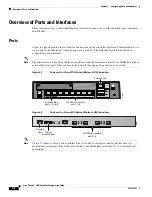
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Memory
The controller contains two kinds of memory: volatile RAM, which holds the current, active controller
configuration, and NVRAM (non-volatile RAM), which holds the reboot configuration. When you are
configuring the operating system in controller, you are modifying volatile RAM; you must save the
configuration from the volatile RAM to the NVRAM to ensure that the controller reboots in the current
configuration.