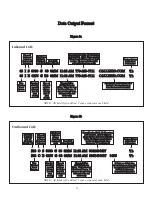
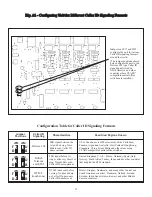
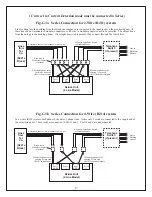
19
Appendix C - RS232 Pin Outs
9 PIN CONNECTIONS
When the serial port is configured to “No Flow Control,” only
Transmit
,
Receive
, and
Ground
connections are
required. Pin 7 and Pin 8 need to be connected only if other serial flow control types are selected.
Computer DB9/M Serial Port
Monitoring Unit DB9/F
Pin
1
(Carrier
Detect)
Pin
1
(No
Connection)
Pin
2
(Receive
)
Pin
2
(Transmit)
Pin
3
(Transmit)
Pin
3
(Receive)
Pin 4 (Data Term. Ready)
Pin 4 (No Connection)
Pin
5
(Ground)
Pin
5
(Ground)
Pin 6 (Data Set Ready)
Pin 6 (Control Line between Units)
Pin 7 (Request to Send)
Pin 7
(Internal
Pin 8 (Clear to Send)
Pin 8
Connection)
Pin
9
(Ring
Indicator)
Pin
9
(No
Connection)
APPLICATION NOTES
Pin 6 is connected only between multiple Whozz Calling? units and acts as a control line. When units are not
transmitting data this line resides at -9 VDC. Upon transmit, the unit pulls this line to +9 VDC. Other Whozz
Calling? units connected will detect this as a busy condition and will not transmit until the line returns to -9 VDC.
If your application program is designed to perform software controlled real time call blocking/passing through a
serial connection, it is important that the Pin 6 control line is at the very least, monitored for the busy condition.
Since units cannot transmit and receive data at the same time, any commands that are issued by the software must be
sent while units are not transmitting. The best solution is to monitor the control line on Pin 4 and pull it high with
Pin 6 when your software is transmitting. This method will assure that commands sent to units will get through.
This line should be pulled high by your serial port through a standard 1N4148 diode as diagrammed below.
Computer 9 Pin Serial Port
CallerID.com Female DB9
Pin 6 (Data Set Ready)
Pin 6 (Control Line)
1N4148
Pin 4 (Data Terminal Ready)