About this product 21/64
RE 92750-01-B/06.2018, A10VG, Series 10,
Bosch Rexroth AG
5.2.2 Functional description
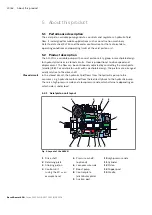
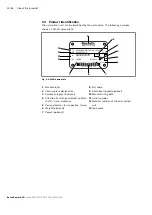
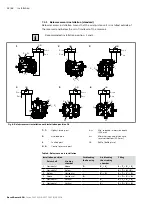
Torque and rotational speed are applied to the drive shaft (1) by a drive motor.
The drive shaft is connected to the cylinder (11) by splines, causing the cylinder to
rotate. With every revolution, the pistons (12) complete a stroke in the cylinder
bores, the size of which depends on the pitch of the cradle (14). The slipper
pads (13) are held on with the pistons and guided along the glide surface of the
cradle by the retaining plate (2).
The pitch of the swashplate during a revolution causes each piston to move over the
bottom and top dead centers and back to its initial position. During this sequence,
hydraulic fluid is fed in and drained out through the two control slots in the control
plate (8) according to displacement. On the high-pressure side (10), the hydraulic
fluid is pushed out of the cylinder chamber and into the hydraulic system by the
pistons. At the same time, hydraulic fluid flows into the expanding piston chamber
on the low-pressure side (6). In a closed circuit, this is supported by the return flow
and boost pressure.
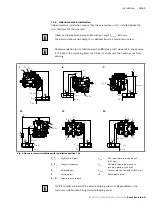
The operating pressure is limited by the pressure cut-off.
The pressure cut-off corresponds to a pressure control which reduces the pump
capacity once the set specified pressure command value is reached so that the set
pressure is maintained but not exceeded.
The two high-pressure relief valves protect the hydrostatic transmission (pump and
motor) from overloading. They limit the maximum pressure in the respective high-
pressure line and serve simultaneously as boost valves. High-pressure relief valves
are not working valves and are only suitable for pressure peaks or high rates of
pressure change.
The boost pump (7) continuously supplies a sufficient volume of fluid (boost volume)
from a small reservoir to the low-pressure side of the closed circuit via a check valve
to replenish the internal leakage of the variable pump and consumer.
The boost pump is an internal gear pump which is driven directly via the drive shaft.
In order to replenish the internal leakage in the variable pump and consumers,
depending on the size or version, the following connections must be connected to an
external source of boost pressure:
• NG18 – port S
• NG28 and 45 – port
G (without DA control valve)
• NG28 and 45 – port
F
e
(with DA control valve)
• NG63 – port F
a
The boost-pressure relief valve is integrated.
The optional sequence valve interrupts the active control pressure. The springs in
the stroking chambers move the stroking piston (3) towards the middle position
(neutral position). The reset function is influenced by the current working pressure
and the rotational speed.
Switching off the control pressure does not ensure that the pump goes to the central
position (neutral position).
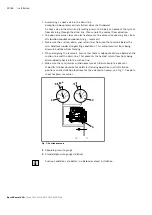
▶
Use an appropriate emergency-off device to ensure that the drive can be brought
to a safe position at any time. The machine or system manufacturer is responsible
for the installation of a proper emergency-off device.
Pump function
Pressure cut-off
High-pressure safeguarding
Version with boost pump
Version without boost
pump (external boost
pressure supply)
Sequence valve
(optional)