Parameterization and commissioning
EL6731
89
Version: 2.8
5.1.6.2.3
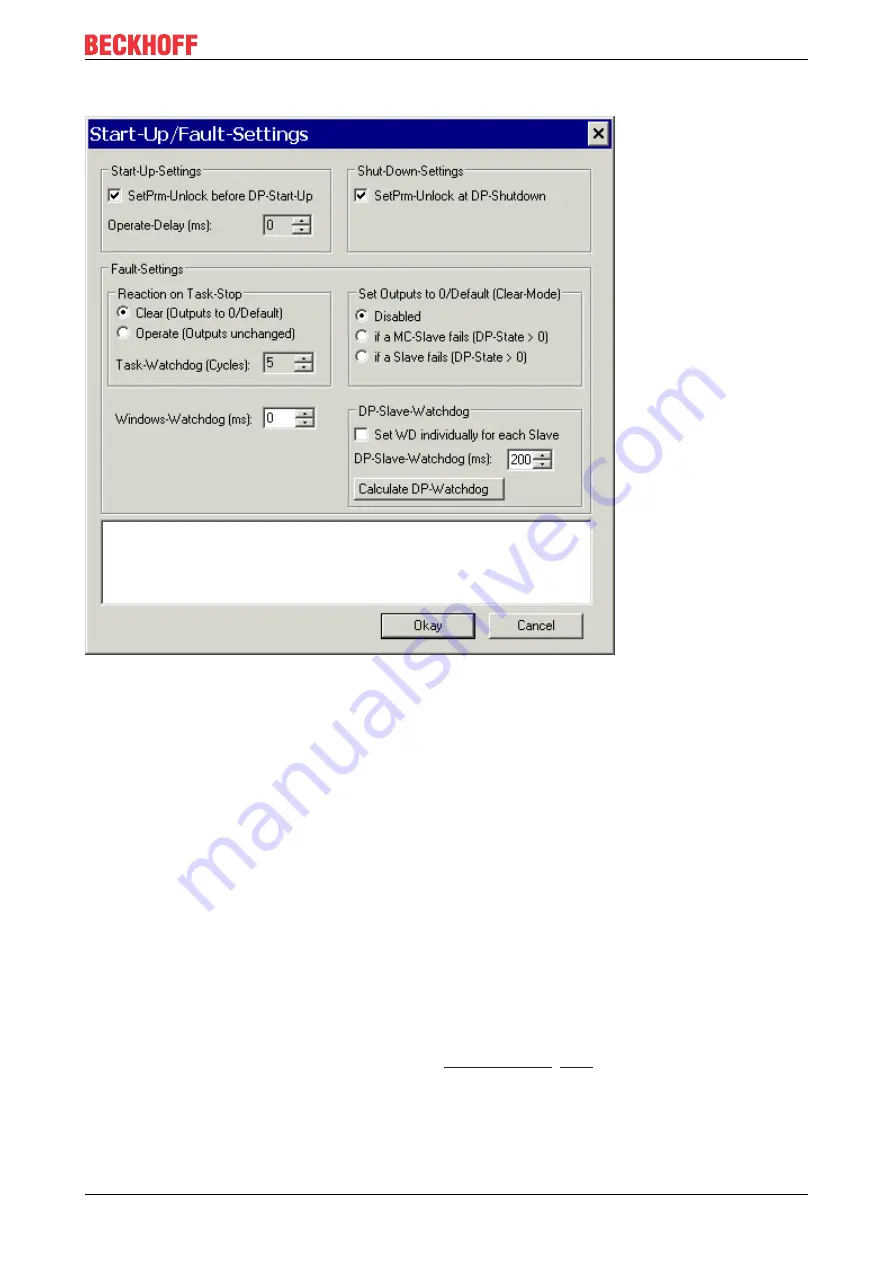
Startup/fault settings dialog
Fig. 89: Startup/fault settings dialog
SetPrm unlock before DP start-up
Normally, during DP start-up, the DP master removes the cyclic connections, so that the DP slave can
always recognize that the DP master has restarted. In redundancy mode, however, it may be specifically
desirable for the DP slave to remain unaware of this, because the switch-over from the primary master to the
redundant master should not have any interactions for the DP slave (see the Master Redundancy section).
SetPrm unlock at DP shutdown
Normally, during DP shut-down, the DP master removes the cyclic connections, so that the DP slave can
always recognize that the DP master has stopped. In redundancy mode, however, it may be specifically
desirable for the DP slave to remain unaware of this, because the switch-over from the primary master to the
redundant master should not have any interactions for the DP slave (see the Master Redundancy section).
Operate delay
The DP master changes automatically, observing the Auto-Clear-Mode, into the operate state when the task
is started. The transition from Clear to Operate can be delayed or with the Operate delay time. In the Clear
state, all the outputs are set to 0 (if the DP slave does not support Fail_Safe values) or to the Fail_Safe value
(if the DP slave supports Fail_Safe), whereas in the Operate state the outputs have the values specified by
the task.
Response to task STOP
It is possible to specify here whether the DP master should set the outputs to 0 when reaching a PLC stop or
breakpoint, or should leave them unchanged (see the
section).
Task watchdog (EtherCAT watchdog)
The DP master changes automatically into the clear mode (the outputs of the slaves are set either to 0 or to
the fail-safe value) when it ceases to receive an interrupt from the associated task (e.g. a PLC breakpoint






























