Commissioning
EL3632
172
Version: 2.8
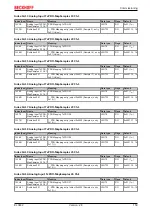
Index F010 Module list
Index (hex) Name
Meaning
Data type
Flags
Default
F010:0
Module list
Maximum subindex
UINT8
RW
0x03 (3
dec
)
F010:01
SubIndex 001
Profile AI
UINT32
RW
0x0000012C
(300
dec
)
F010:02
SubIndex 002
Profile AI
UINT32
RW
0x0000012C
(300
dec
)
F010:03
SubIndex 003
Profile AI
UINT32
RW
0x0000012C
(300
dec
)
5.7
Notices on analog specifications
Beckhoff I/O devices (terminals, boxes, modules) with analog inputs are characterized by a number of
technical characteristic data; refer to the technical data in the respective documents.
Some explanations are given below for the correct interpretation of these characteristic data.
5.7.1
Full scale value (FSV)
An I/O device with an analog input measures over a nominal measuring range that is limited by an upper and
a lower limit (initial value and end value); these can usually be taken from the device designation.
The range between the two limits is called the measuring span and corresponds to the equation (end value -
initial value). Analogous to pointing devices this is the measuring scale (see IEC 61131) or also the dynamic
range.
For analog I/O devices from Beckhoff the rule is that the limit with the largest value is chosen as the full scale
value of the respective product (also called the reference value) and is given a positive sign. This applies to
both symmetrical and asymmetrical measuring spans.
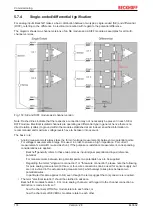
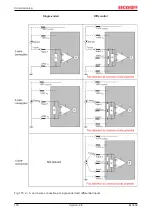
Fig. 171: Full scale value, measuring span
For the above
examples
this means:
• Measuring range 0...10 V: asymmetric unipolar, full scale value = 10 V, measuring span = 10 V
• Measuring range 4...20 mA: asymmetric unipolar, full scale value = 20 mA, measuring span = 16 mA
• Measuring range -200...1370°C: asymmetric bipolar, full scale value = 1370°C, measuring
span = 1570°C
• Measuring range -10...+10 V: symmetric bipolar, full scale value = 10 V, measuring span = 20 V
This applies to analog output terminals/ boxes (and related Beckhoff product groups).
5.7.2
Measuring error/ measurement deviation
The relative measuring error (% of the full scale value) is referenced to the full scale value and is calculated
as the quotient of the largest numerical deviation from the true value (‘measuring error’) referenced to the full
scale value.