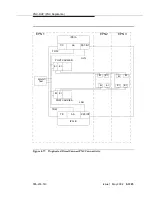
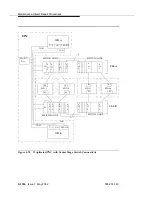
Maintenance-Object Repair Procedures
555-233-143
8-1294
Issue 1 May 2002
interchange will occur during the repair of the standby PNC. The demand
interchange may not be necessary if the following conditions drive a
spontaneous interchange:
■
The anti-thrashing period from the last interchange has expired.
■
The global refresh from releasing the standby PNC has completed.
The standby PNC SOH is better than the active.
3. At this point, the faulty component will be on the standby PNC, and the
PNCs are locked in their current active/standby state. Busy-out the PNC.
Then fault isolation and component testing procedures for the individual
PNC components can be used just as for an unduplicated PNC.
Replacement of components will not disrupt operation of the active PNC.
4. Once the failed component is replaced, test the standby PNC component
from the terminal to ensure the replacement is functioning properly.
5. When confident that the problem has been resolved, as indicated by a
state of health with all zeros, (status pnc), unlock and release the pnc.
Note that no further PNC interchange is required since you can test the
standby PNC as thoroughly as the active.
Interactions: Media Server Resets and PNC
Interchanges
■
A system reset of level 1 (warm), 2 (cold2) or 4 (reboot) does not change
which PNC is active. If a PNC interchange was in progress when the reset
took place, the PNC interchange still goes to completion.
■
If a system reset level 1 (warm) takes place during a PNC interchange, the
reset is escalated to level 2 (cold2).
Fault Isolation Using Duplicated PNC
PNC duplication, can, in some cases aid in the isolation of faults. PNC
interchanges can be used to help indict the faulty hardware. Following are two
examples demonstrating this technique.
■
There is a fault which can occur in either an IPSI port network’s EI or the
PKT-INT which cannot be readily attributed to one board or the other. If the
packet bus transceivers on either the PKT-INT or EI fail, it will be apparent
that the two boards cannot communicate, but it will not be clear which
board is at fault. In this case, a planned interchange of the PNC can be
used to indict one of the two boards. If the interchange cures the problem,
the EI was at fault. If the interchange does not cure the problem, the
PKT-INT is suspect, provided there are no PKT-BUS faults.
■
A similar relationship exists for the PN Archangel (active EI) and certain
TDM bus problems. If the EAA is unable to communicate with a port board
over the TDM bus, either the EAA has a fault, the port board has a fault, or
there is a problem with the TDM bus itself. If TDM bus maintenance tests
Содержание S8700 Series
Страница 50: ...Maintenance Architecture 555 233 143 1 26 Issue 1 May 2002 ...
Страница 74: ...Initialization and Recovery 555 233 143 3 12 Issue 1 May 2002 ...
Страница 186: ...Alarms Errors and Troubleshooting 555 233 143 4 112 Issue 1 May 2002 ...
Страница 232: ...Additional Maintenance Procedures 555 233 143 5 46 Issue 1 May 2002 ...
Страница 635: ...status psa Issue 1 May 2002 7 379 555 233 143 status psa See status tti on page 7 406 ...
Страница 722: ...Maintenance Commands 555 233 143 7 466 Issue 1 May 2002 ...
Страница 1121: ...CARR POW Carrier Power Supply Issue 1 May 2002 8 399 555 233 143 Figure 8 19 Power Distribution Unit J58890CH 1 ...
Страница 1447: ...E DIG RES TN800 reserve slot Issue 1 May 2002 8 725 555 233 143 E DIG RES TN800 reserve slot See ASAI RES ...
Страница 1735: ...LGATE AJ Issue 1 May 2002 8 1013 555 233 143 LGATE AJ See BRI SET LGATE BD See BRI BD LGATE PT See BRI PT ...
Страница 1846: ...Maintenance Object Repair Procedures 555 233 143 8 1124 Issue 1 May 2002 Figure 8 62 TN787 MMI MULTIMEDIA INTERFACE CIRCUIT PACK ...