Aruba AP-103H Wireless Access Point
The Aruba AP-103H wireless access point that supports the IEEE 802.11n
standard for high-performance WLAN. This access point uses MIMO (Multiple-
Input, Multiple-Output) technology and other high-throughput mode techniques
to deliver high-performance, 802.11n 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz functionality while
simultaneously supporting existing 802.11a/b/g wireless services. The AP-103H
access point works only in conjunction with an Aruba Controller.
The Aruba AP-103H access point provides the following capabilities:
Wireless transceiver
Protocol-independent networking functionality
IEEE 802.11a/b/g/n operation as a wireless access point
IEEE 802.11a/b/g/n operation as a wireless air monitor
Compatibility with IEEE 802.3af PoE
Central management configuration and upgrades through an Aruba
Controller
Package Contents
AP-103H Access Point
Single Gang Wall-box Mounting bracket
2x Mount Screws
Installation Guide (this document)
Hardware Overview
Figure 1
Front
LED
The AP-103H is equipped with one LED that indicates the system status of the
AP.
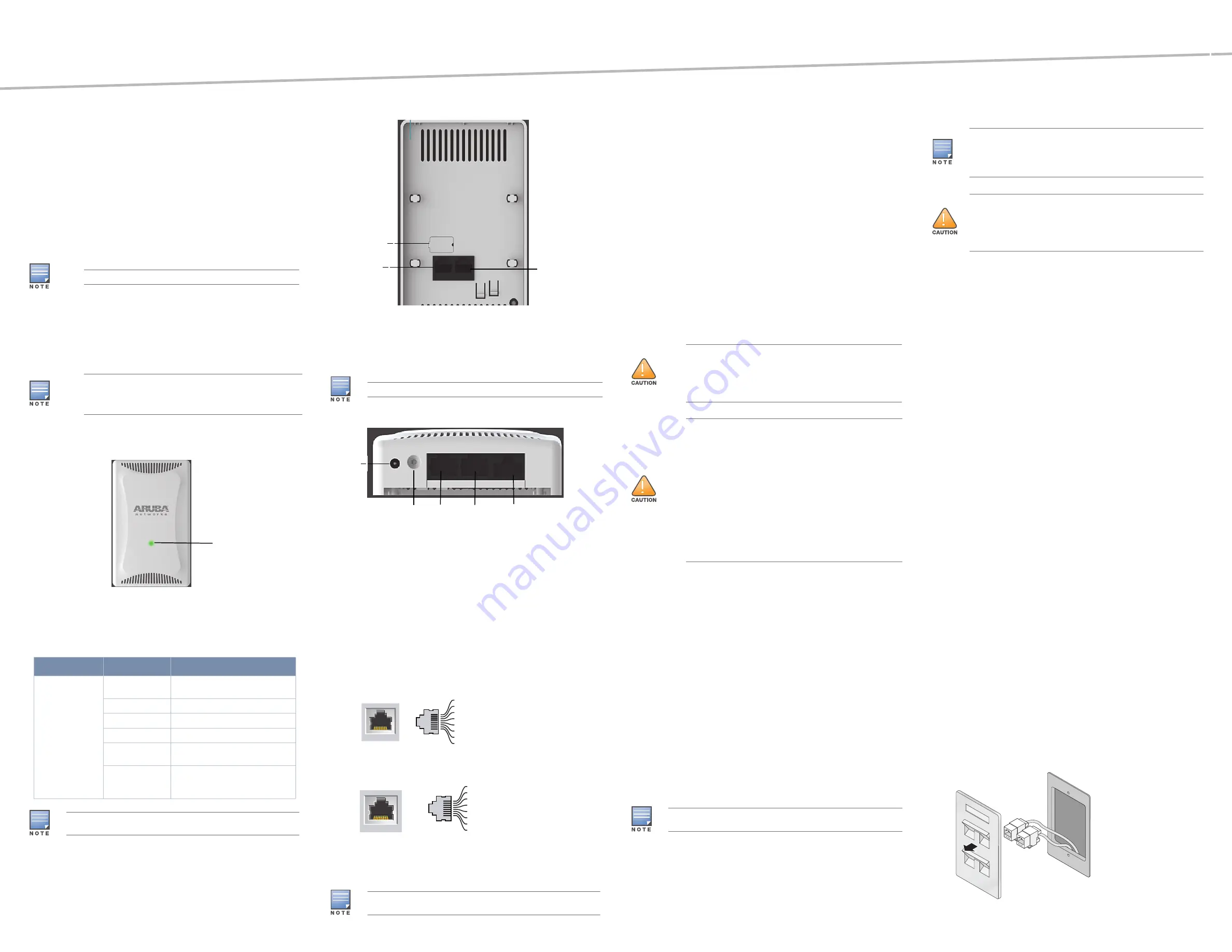
Figure 2
Rear
Console Port
The serial console port allows you to connect the AP to a serial terminal or a
laptop for direct local management. This port is a 4-pin connector covered by a
dust cover. An optional serial adapter cable (AP-CBL-SER) is available for use
with the IAP-103 and is sold separately.
Figure 3
Bottom
Ethernet Ports
AP-103H is equipped with a total of three active Ethernet ports (ENET 0-2).
ENET 0 is a 10/100/1000Base-T (RJ-45) auto-sensing, MDI/MDX wired-network
uplink connectivity port. This port supports IEEE 802.3af Power over Ethernet
(PoE), accepting 48VDC as a standard defined Powered Device (PD) from a
Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE) such as a PoE midspan injector or network
infrastructure that supports PoE. ENET 1 and 2 are 10/100Base-T (RJ-45) auto-
sensing, MDI/MDX wired-network downlink connectivity ports, used to provide
secure network connectivity to wired devices. ENET 0 is located on the rear of
the AP, while ENET 1 and 2 are located on the bottom (
).
Additionally, AP-103H supports a passive pass-through RJ-45 interface to extend
a physical connection (typically another Ethernet connection) from the back of
the device to a connector on the bottom.
Figure 4
Gigabit Ethernet Port Pin-Out
Figure 5
Fast Ethernet Port Pin-Out
DC Power Socket
The AP-103H has a single 12V DC power jack socket to support powering
through an AC-to-DC power adapter.
Push Button
The push button can be used to reset the AP to factory default settings or turn
off/on the System Status LED.
To reset the AP to factory default settings:
1. Power off the AP.
2. Press and hold the push button using a small, narrow object, such as a
paperclip.
3. Power-on the AP without releasing the push button. The system status
LED will flash within 5 seconds.
4. Release the push button.
The system status LED will flash again within 15 seconds indicating that the
reset is completed. The AP will now continue to boot with the factory default
settings.
To turn off/on the system status LED:
During the normal operation of the AP, press the push button using a small,
narrow object, such as a paperclip. The system status LED will be turned off/
on immediately.
Before You Begin
Pre-Installation Network Requirements
After WLAN planning is complete and the appropriate products and their
placement have been determined, the Aruba controller(s) must be installed and
initial setup performed before the Aruba APs are deployed.
AP Pre-Installation Checklist
Before installing your AP-103H access point, be sure that you have the following:
Pre-installed wall box
Cat5 UTP cable with network access installed in the wall box
One of the following power sources:
IEEE 802.3af-compliant Power over Ethernet (PoE) source
Aruba AP AC-DC adapter kit (sold separately)
Aruba Controller provisioned on the network:
Layer 2/3 network connectivity to your access point
One of the following network services:
Aruba Discovery Protocol (ADP)
DNS server with an “A” record
DHCP Server with vendor-specific options
Summary of the Setup Process
Successful setup of an AP-103H access point consists of five tasks, which must
be performed in this order:
1. Verify pre-installation connectivity.
2. Identify the specific installation location for each AP.
3. Install each AP.
4. Verify post-installation connectivity.
5. Configure each AP.
Verifying Pre-Installation Connectivity
Before you install APs in a network environment, make sure that the APs are
able to locate and connect to the controller after power on. Specifically, you
must verify the following conditions:
When connected to the network, each AP is assigned a valid IP address
APs are able to locate the controller
Refer to the
ArubaOS Quick Start
Guide for instructions on locating and
connecting to the controller.
Identifying Specific Installation Locations
You can mount the AP-93H access point on a wall or on the ceiling. Use the AP
placement map generated by Aruba’s RF Plan software application to determine
the proper installation location(s). Each location should be as close as possible
to the center of the intended coverage area and should be free from obstructions
or obvious sources of interference. These RF absorbers/reflectors/interference
sources will impact RF propagation and should have been accounted for during
the planning phase and adjusted for in RF plan.
Identifying Known RF Absorbers/Reflectors/Interference
Sources
Identifying known RF absorbers, reflectors, and interference sources while in
the field during the installation phase is critical. Make sure that these sources are
taken into consideration when you attach an AP to its fixed location.
RF absorbers include:
Cement/concrete—Old concrete has high levels of water dissipation, which
dries out the concrete, allowing for potential RF propagation. New concrete
has high levels of water concentration in the concrete, blocking RF signals.
Natural Items—Fish tanks, water fountains, ponds, and trees
Brick
RF reflectors include:
Metal Objects—Metal pans between floors, rebar, fire doors, air conditioning/
heating ducts, mesh windows, blinds, chain link fences (depending on
aperture size), refrigerators, racks, shelves, and filing cabinets.
Do not place an AP between two air conditioning/heating ducts. Make sure
that APs are placed below ducts to avoid RF disturbances.
RF interference sources include:
Microwave ovens and other 2.4 or 5 GHz objects (such as cordless phones)
Cordless headset such as those used in call centers or lunch rooms
Installing the AP
The AP-103H is designed to mount into a variety of electrical gang boxes. To
install your AP-103H:
1. Begin by removing the existing data wall plate (if applicable).
Figure 6
Removing Wall Plate (Standard US Single Gang Outlet Box Shown)
The Aruba AP-103H requires ArubaOS
6.4.1
or later.
Inform your supplier if there are any incorrect, missing, or damaged
parts. If possible, retain the carton, including the original packing
materials. Use these materials to repack and return the unit to the
supplier if needed.
Table 1
LED Meanings
LED
Color/State
Meaning
System Status LED
Off
No power to AP, or LED switched to
‘off mode’
Red
Error condition
Green - Flashing
LED switched to ‘blink mode’
Green - Steady
AP ready
Amber - Flashing
AP booting, or AP in Air or Spectrum
monitor mode
Amber - Steady
AP ready, restricted mode:
10/100Mbps uplink negotiated
Either radio in non-HT mode
For more information on blink and off mode of the LED, refer to the
ArubaOS User Guide
.
System Status LED
The console port does not support hot-plug operation.
If both POE and DC power are available, the AP uses DC power, but a
small current will be drawn from the POE power source as well.
Console Port
Pass Through
Port
ENET0
DC
Power
Push Button
ENET1
ENET2
Pass Through Port
1000Base-T Gigabit
Ethernet Port
RJ-45 Female
Pin-Out
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Spare Pair
Spare Pair
Spare Pair
Spare Pair
ETH Rx+
ETH Rx-
ETH Tx+
ETH Tx-
(POE positive)
(POE positive)
(POE negative)
(POE negative)
(POE negative)
(POE negative)
(POE positive)
(POE positive)
10/100 Mbps Ethernet
e
e
n
t
Spare Pair
Spare Pair
Spare Pair
Spare Pair
1
ETH Tx+
ETH Tx–
ETH Rx+
ETH Rx–
FCC Statement:
Improper termination of access points installed in
the United States configured to non-US model controllers will be in
violation of the FCC grant of equipment authorization. Any such willful
or intentional violation may result in a requirement by the FCC for
immediate termination of operation and may be subject to forfeiture
(47 CFR 1.80).
EU Statement:
Lower power radio LAN product operating in 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz
bands. Please refer to the
ArubaOS User Guide
for details on
restrictions.
Produit réseau local radio basse puissance operant dans la bande
fréquence 2.4 GHz et 5 GHz. Merci de vous referrer au
ArubaOS User
Guide
pour les details des restrictions.
Low Power FunkLAN Produkt, das im 2.4 GHz und im 5 GHz Band
arbeitet. Weitere Informationen bezlüglich Einschränkungen finden
Sie im
ArubaOS User Guide.
Apparati Radio LAN a bassa Potenza, operanti a 2.4 GHz e 5 GHz.
Fare riferimento alla
ArubaOS User Guide
per avere informazioni
detagliate sulle restrizioni.
It is important that you verify the items listed under
before you attempt to set up and install an AP-103H.
Aruba Networks, Inc., in compliance with governmental requirements, has
designed the AP-93H access points so that only authorized network
administrators can change the settings. For more information about AP
configuration, refer to the
ArubaOS Quick Start Guide and ArubaOS User
Guide
.
Access points are radio transmission devices and as such are subject to
governmental regulation. Network administrators responsible for the
configuration and operation of access points must comply with local
broadcast regulations. Specifically, access points must use channel
assignments appropriate to the location in which the access point will be
used.


