DMA Controller
9-13
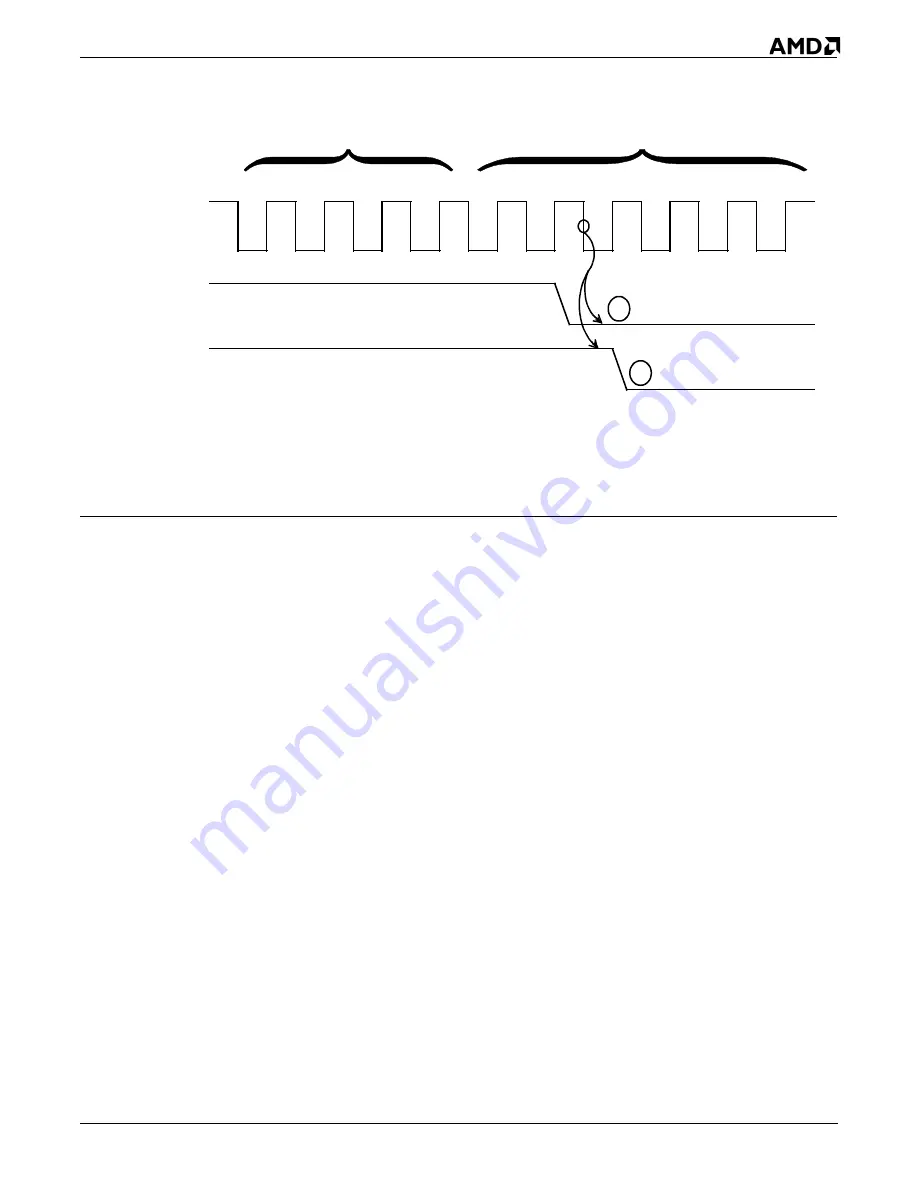
Figure 9-9
Destination Synchronized DMA Transfers
Notes:
1. This destination-synchronized transfer is not followed immediately by another DMA transfer.
2. This destination-synchronized transfer is immediately followed by another DMA transfer because
DRQ is not deasserted soon enough.
9.4.2
DMA Acknowledge
No explicit DMA acknowledge signal is provided. Since both source and destination
registers are maintained, a read from a requesting source or a write to a requesting
destination should be used as the DMA acknowledge signal. Since the chip-select lines
can be programmed to be active for a given block of memory or I/O space, and the DMA
source and destination address registers can be programmed to point to the same given
block, a chip-select line could be used to indicate a DMA acknowledge.
9.4.3
DMA Priority
The DMA channels can be programmed so that one channel is always given priority over
the other, or they can be programmed to alternate cycles when both have DMA requests
pending (see Section 9.3.1, bit 5, the P bit). DMA cycles always have priority over internal
CPU cycles except between locked memory accesses or word accesses to odd memory
locations. However, an external bus hold takes priority over an internal DMA cycle.
Because an interrupt request cannot suspend a DMA operation and the CPU cannot access
memory during a DMA cycle, interrupt latency time suffers during sequences of continuous
DMA cycles. An NMI request, however, causes all internal DMA activity to halt. This allows
the CPU to respond quickly to the NMI request.
DMA is also suspended during LOCKED bus cycles or during bus holds.
9.4.4
DMA Programming
DMA cycles occur whenever the ST bit of the control register is set. If synchronized transfers
are programmed, a DRQ must also be generated. Therefore, the source and destination
transfer address registers and the transfer count register (if used) must be programmed
before the ST bit is set.
Each DMA register can be modified while the channel is operating. If the CHG bit is set to
0 when the control register is written, the ST bit of the control register will not be modified
T1
T2
T3
T4
T1
T2
T3
T4
CLKOUT
DRQ
(First case)
DRQ
(Second case)
Fetch Cycle
Deposit Cycle
1
2
TI
TI
Содержание Am186 ES
Страница 1: ...Am186 ES and Am188 ES User s Manual...
Страница 4: ...iv...
Страница 12: ...Table of Contents xii...
Страница 22: ...Features and Performance 1 8...
Страница 60: ...System Overview 3 28...
Страница 84: ...Chip Select Unit 5 14...
Страница 132: ...Timer Control Unit 8 8...
Страница 166: ...Programmable I O Pins 11 6...
Страница 184: ...Register Summary A 18...






























