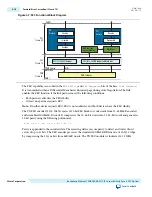
Figure 4-4: TX Equalization in Daisy-Chain Mode
RX
Encode
Handshake
Adapt
TX
dmi*
dmi*
dmi*
dmo*
dmo*
Partner A
Parter C
Parter B
Eq
Decode
RX
Encode
Handshake
Adapt
TX
Eq
Decode
Change Eq
Ack
Change
Data Transmission
Adaptation Feedback
Change Eq
Ack Change
Feedback/Handshake via Management
RX
Encode
Handshake
Adapt
TX
Eq
Decode
Change Eq
Ack Change
1
2
3
4
5
dmo*
Data transmission proceeds clockwise from link partner A, to B, to C. TX equalization includes the
following steps which are identified in the figure :
1. The receiving partner B calculates the BER for data received from transmitting partner A.
2. The receiving partner B sends updates for TX link partner C.
3. The receiving link partner C transmits an update to the transmitting link partner A.
4. Transmit partner A updates its equalization settings.
5. Transmit partner A acknowledges the change.
This procedure is repeated for the other two link partners.
Sequencer
The Sequencer (Rate change) block controls the start-up (reset, power-on) sequence of the PHY IP. It
automatically selects which PCS (1G, 10GbE, or Low Latency) is required and sends requests to
reconfigure the PCS. The Sequencer also performs the parallel detection function that reconfigures
between the 1G and 10GbE PCS until the link is established or times out.
Auto Negotiation (AN), Clause 73
The Auto Negotiation module in the 10GBASE-KR PHY IP implements Clause 73 of the Ethernet
standard. This module currently supports auto negotiation between 1GbE and 10GBASE-R data rates.
UG-01080
2015.01.19
10GBASE-KR PHY IP Core Functional Description
4-13
Backplane Ethernet 10GBASE-KR PHY IP Core with Early Access FEC Option
Altera Corporation
Send Feedback